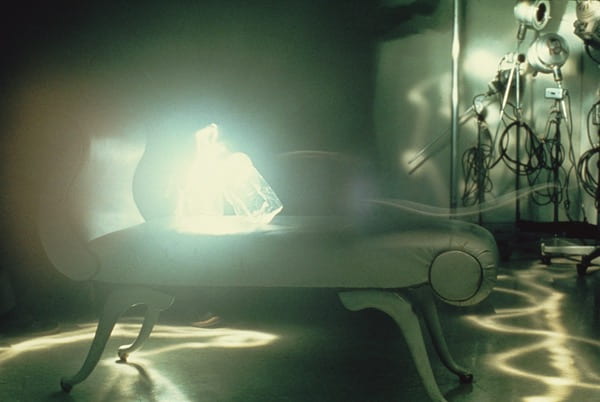
Shona Waldron
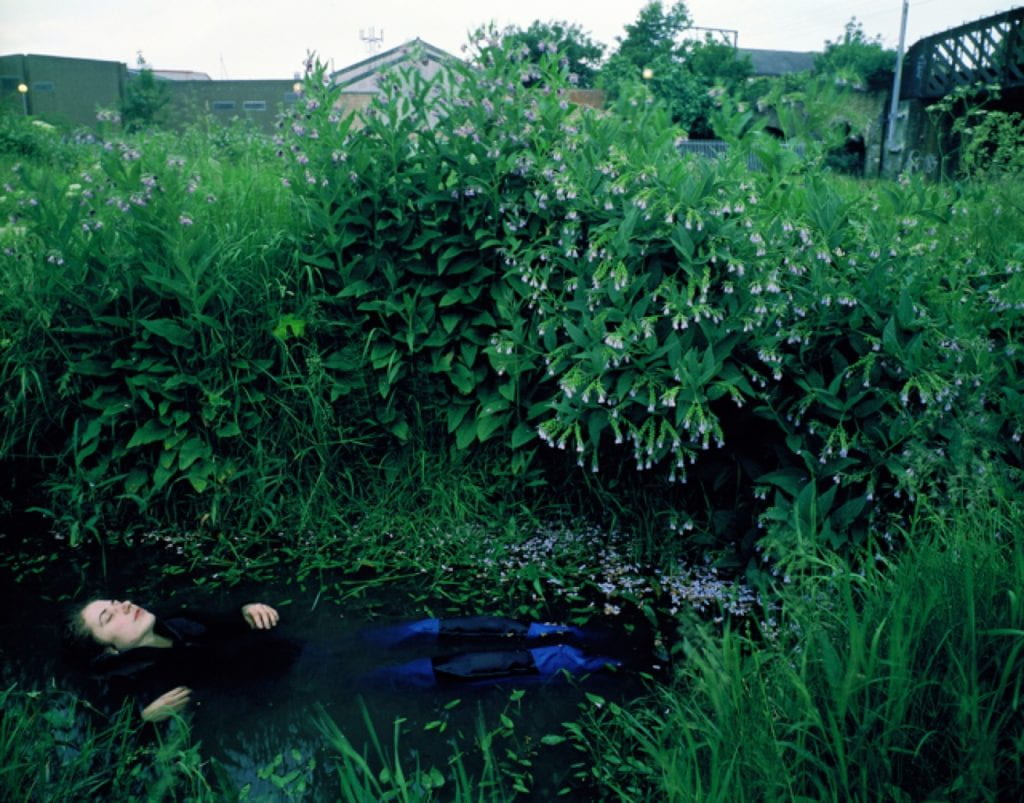
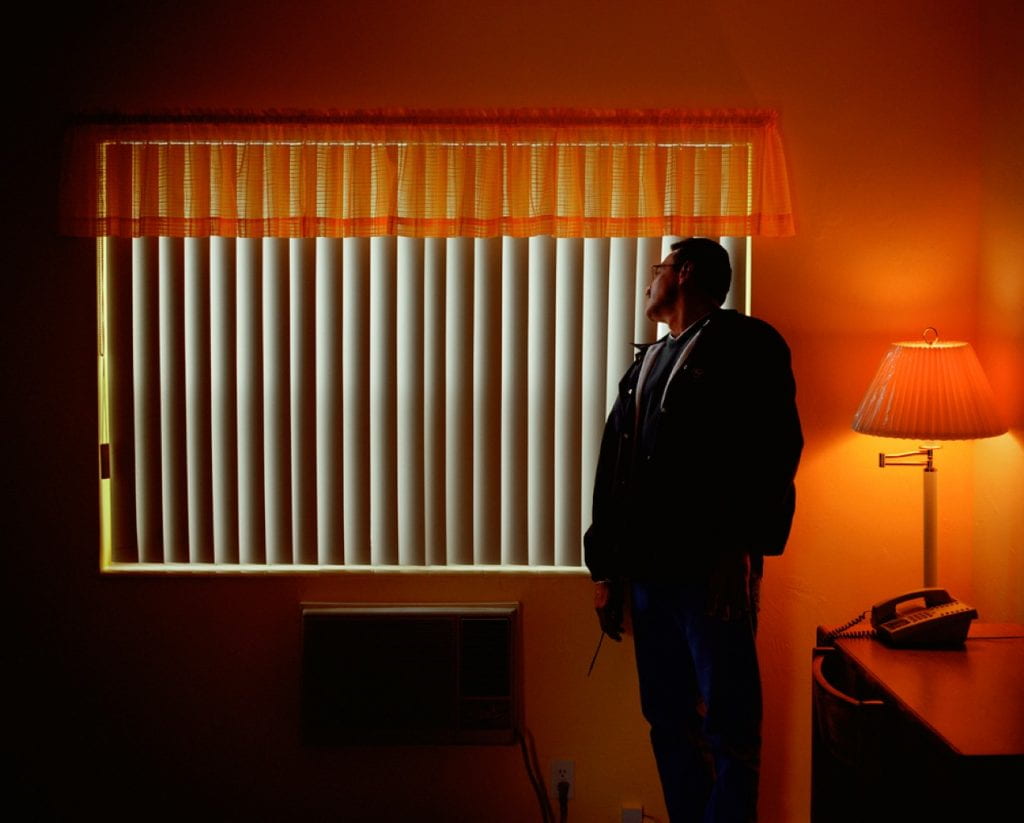
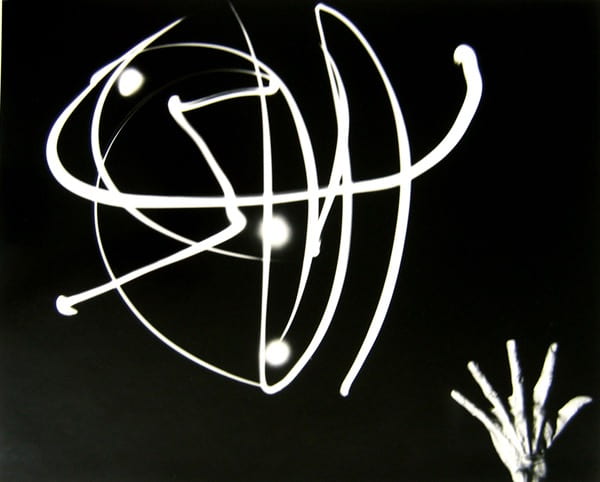
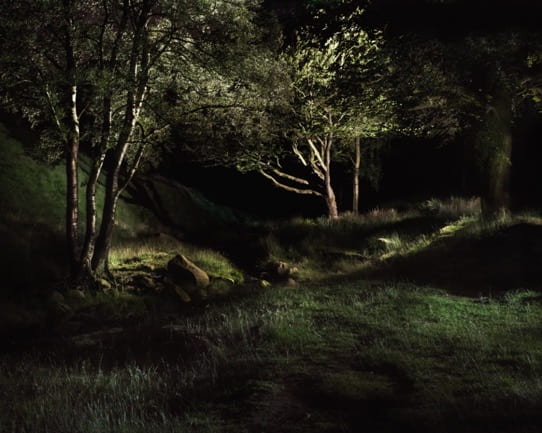
Shona Waldron is an interdisciplinary artist based between East Sussex and Cornwall, UK. Working across a diverse range of media including photography, painting, moving image and installation, she articulates a world of uncertainty, frequently using a combination of digital and analogue techniques to manipulate the periphery of fact and fiction. The blurring of these demarcations plays a crucial role in exploring ideas centred around time, space and the nature of existence, presenting life as a source of wonder and infinite possibility. Investigating states of change or metamorphosis is also a recurrent theme as she uses her work to illustrate the transition into a future which is impossible to predict or control.
Follow Shona Waldron on instagram
Primordial Loop from Shona Waldron on Vimeo.
Shona Waldron Sensorium
24th – 28th June 2021
The Fish Factory, Penryn, Cornwall
Private View: 24th June 2021: 6pm – 9pm
BtL: Your upcoming exhibition Sensorium opens on the 24th June 2021. It brings together works from several of your recent projects. Can you sum up any overall themes in your practice?
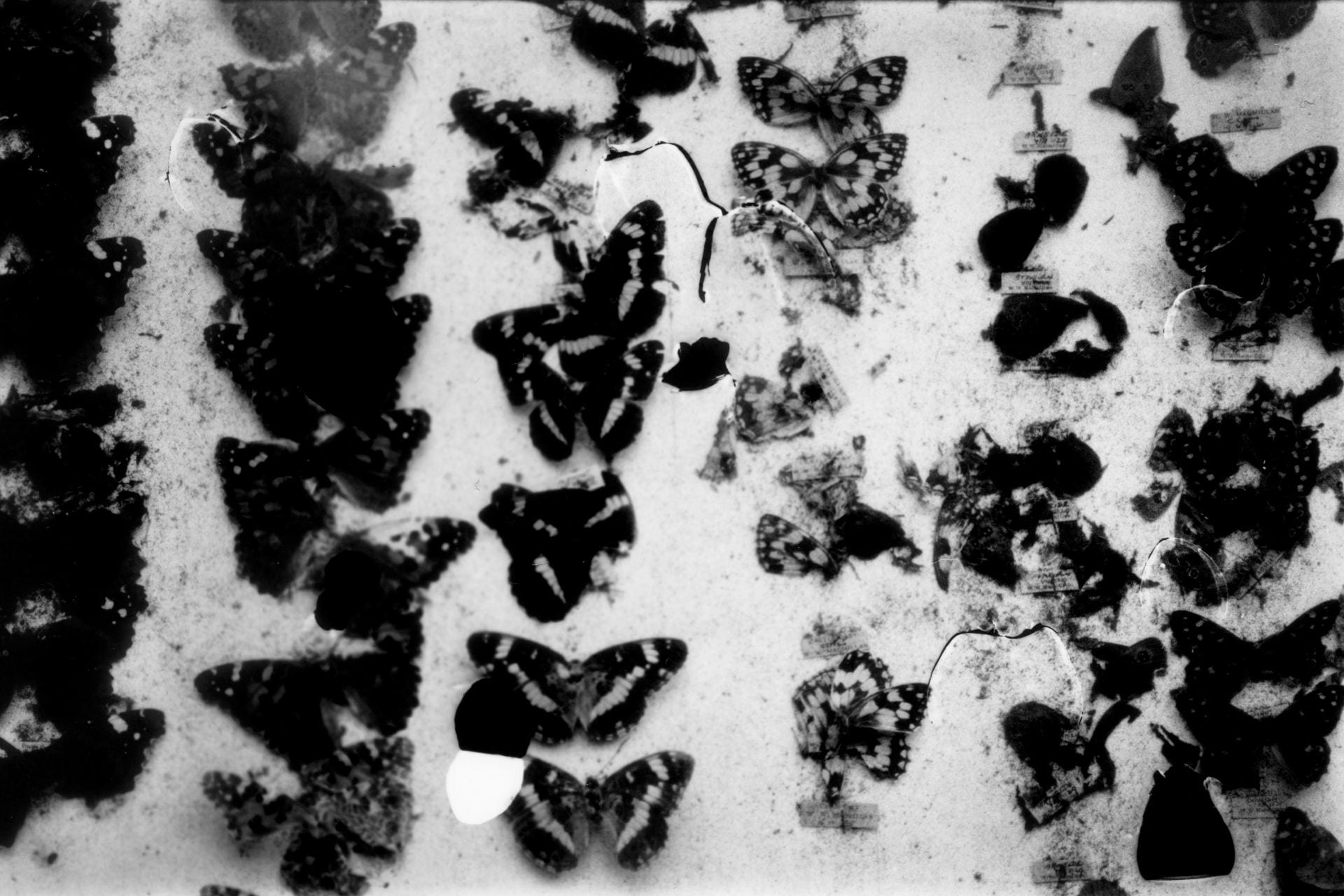
SW: Sensorium is a collection of work that encompasses moving image, photography, painting and installation. The title draws inspiration from the sensory apparatus of the human body which is responsible for receiving and interpreting external stimuli. Intended to be viewed as part of an immersive experience, each exhibited piece explores themes surrounding the intersection of art, science and technology, evoking the idea of new realities that are activated by our perceptual encounters with the space.
Although my work often makes reference to scientific language and taxonomical systems, there is equally a free-flowing element that induces feelings of fluidity and life in a constant cycle of evolution. There are also parallels made between the organic and the technical, with a blending together of analogue and digital media to allow the subject matter to exist in a transformed state that surpasses the limits of its original definition.
BtL: You seem to be interested in visually exploring the relationship between the technological world and the natural world. Why is it important for you to incorporate a range of media into your practice?
SW: The incorporation of a variety of media and processes is definitely very important. I find that moving beyond the boundaries of a purely photographic practice allows the work to function in a universal context which is useful when dealing with these expansive and broad themes. This mixed media approach makes it easier for my work to emphasise connections on multiple levels, whether it be visual, auditory or as an entire sensorial experience. I think this way of working is helpful in creating a sense of dynamism, something that is of particular interest in light of my ideas surrounding the mutable relationship between technological and biological forms.
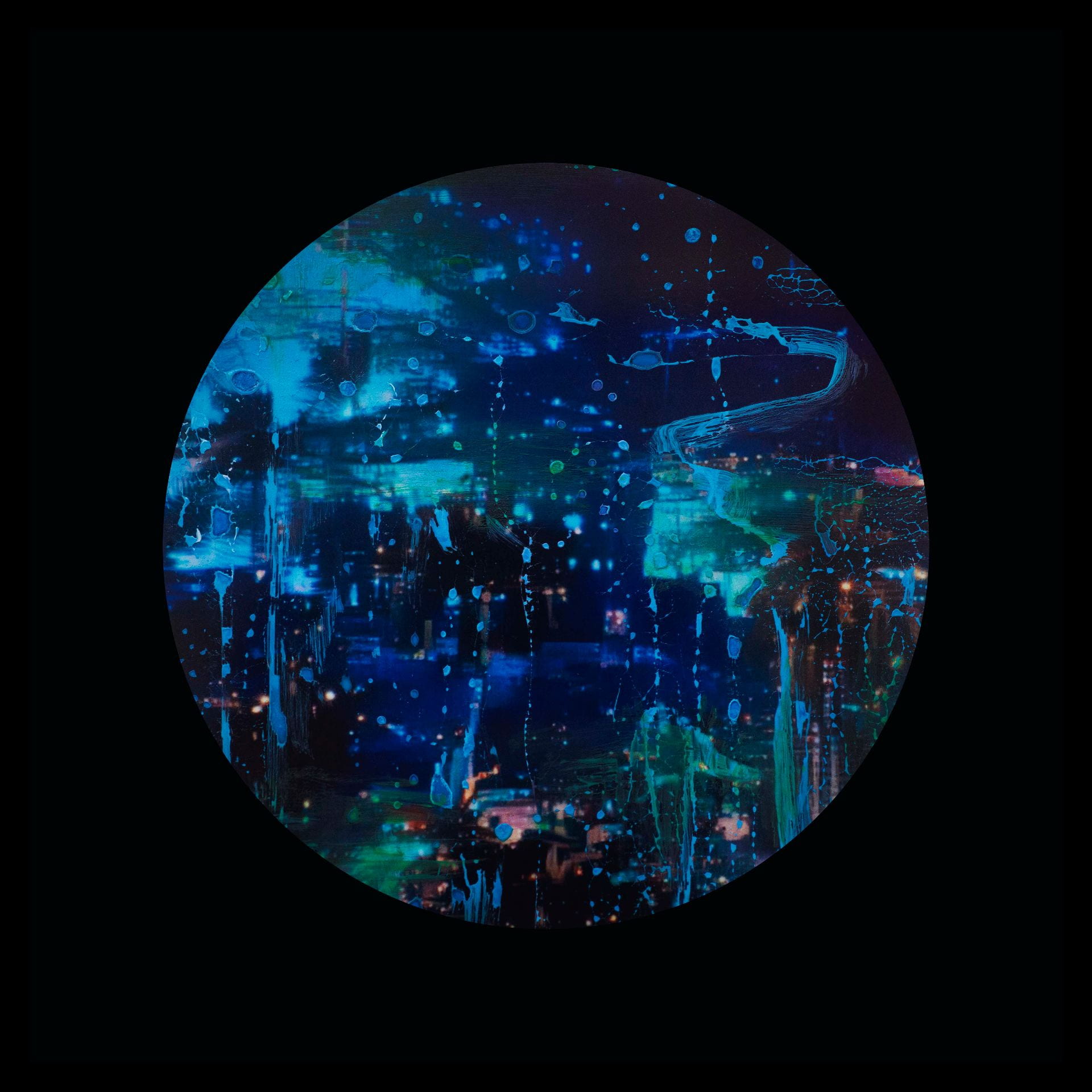

BtL: The title of your video work Primordial Loop seems to both juxtapose and connect the idea of new possibilities / the inter-connectedness of man and machine; the technical and the organic…
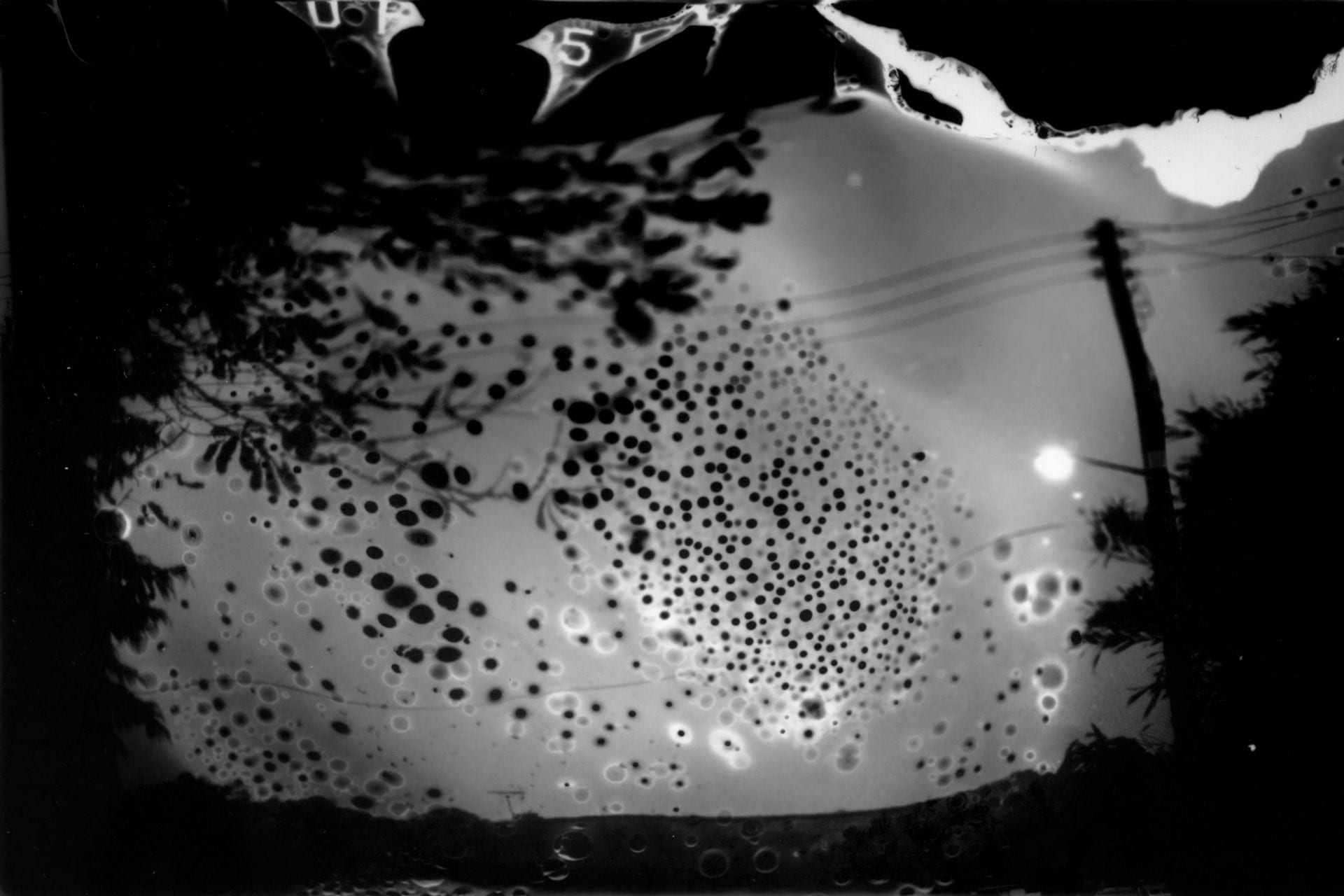
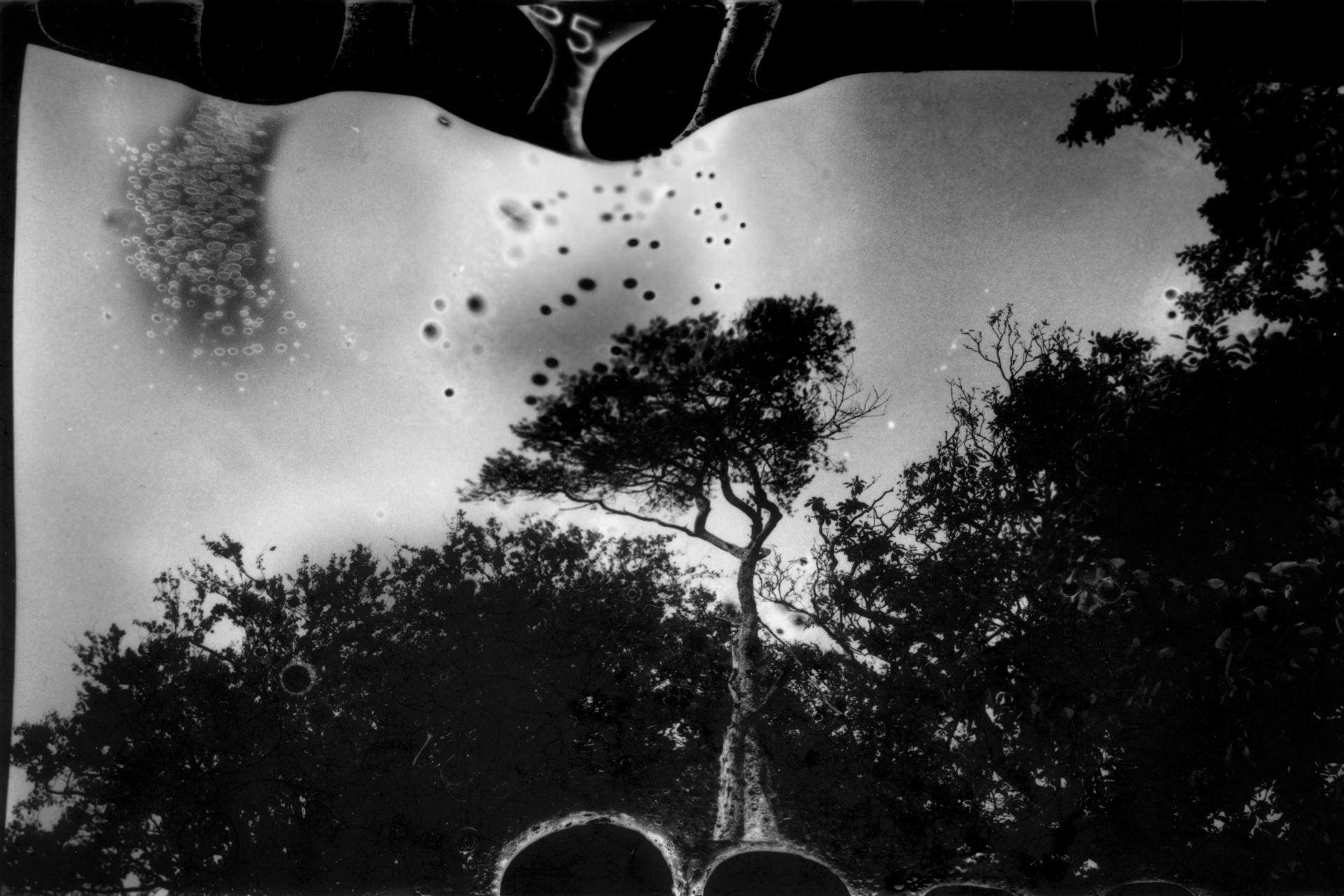
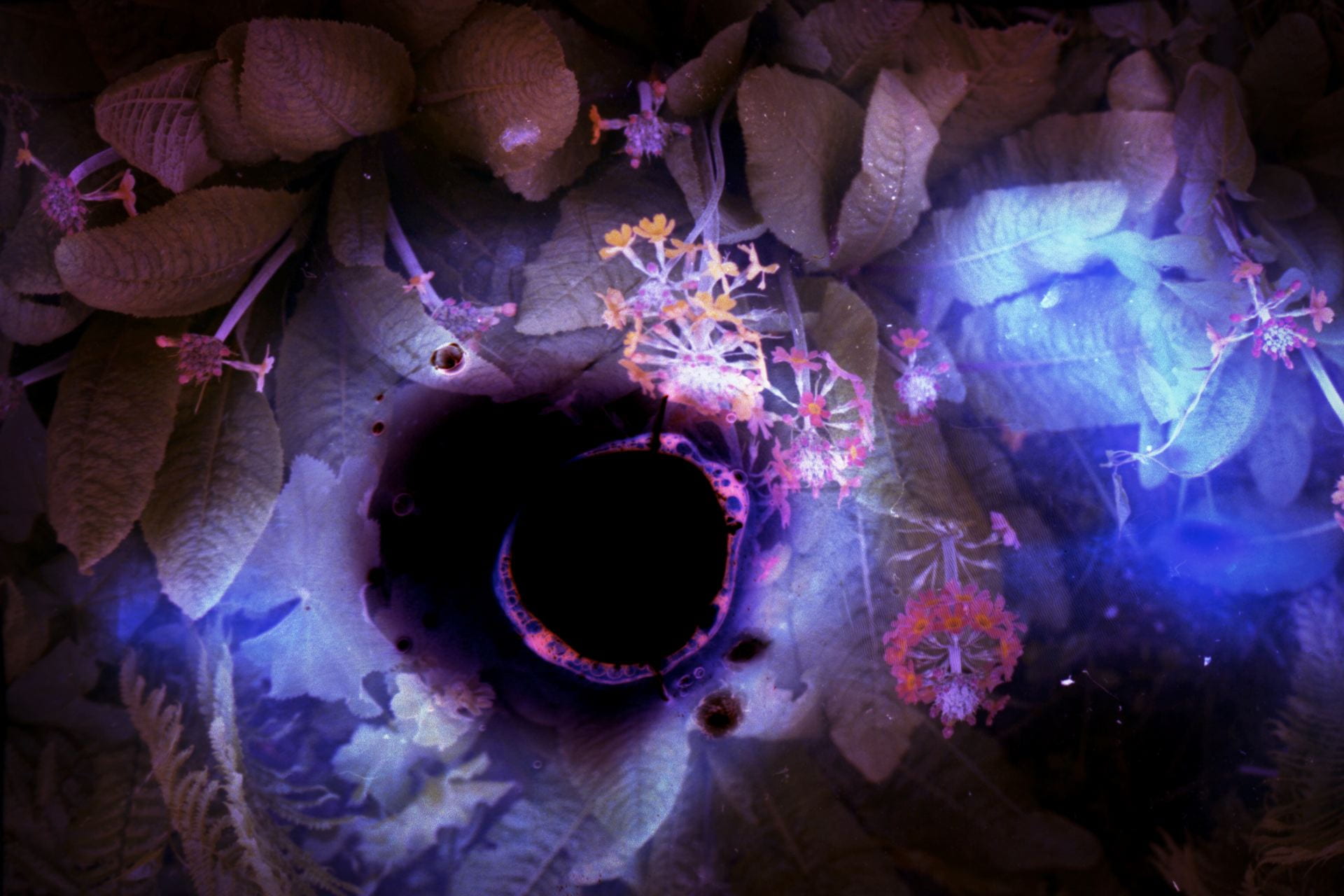
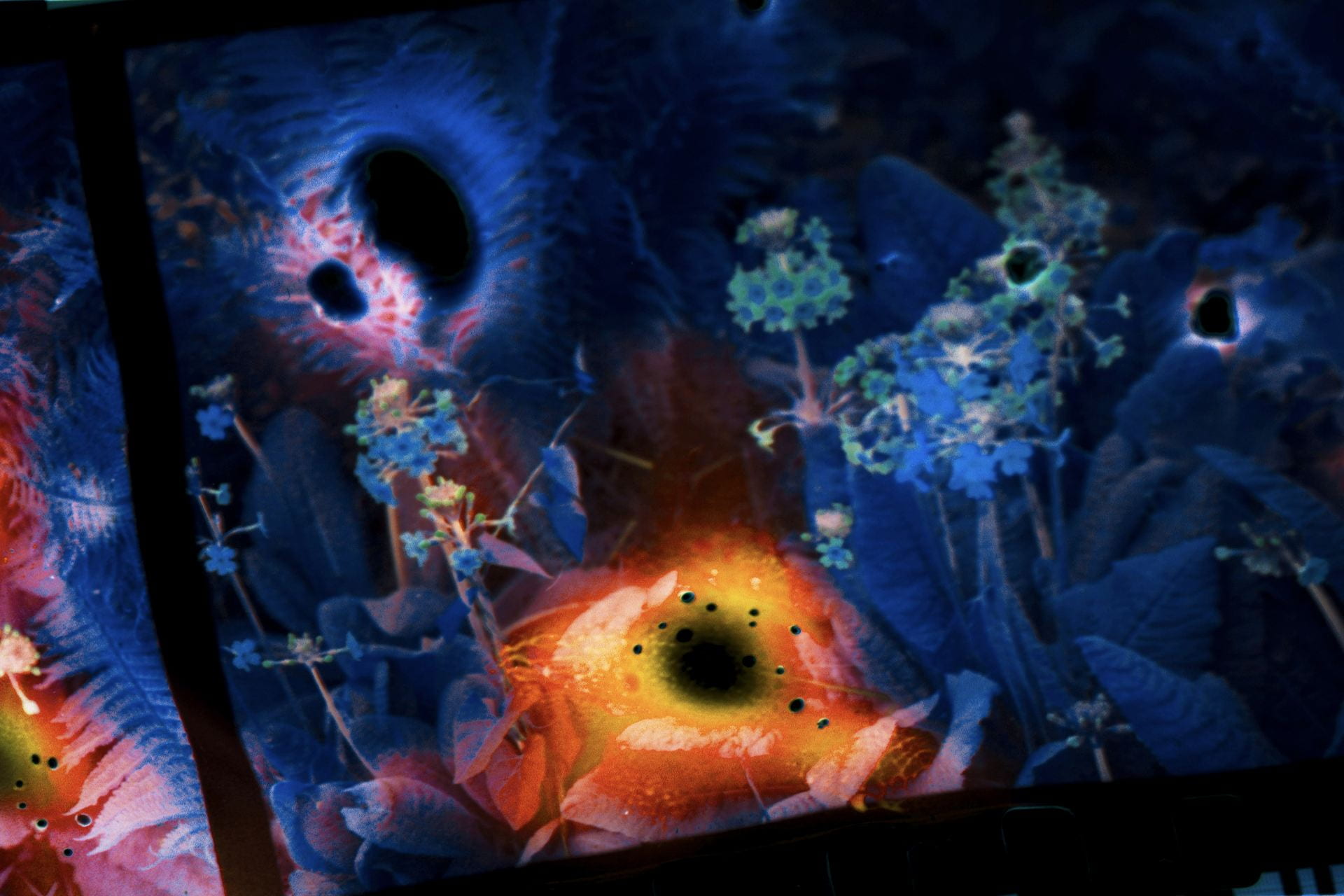
SW: Primordial Loop is an experimental video piece that incorporates 3D modelling and animation. Its title draws inspiration from ‘primordial soup’, a term often used to refer to the blend of biological conditions that first enabled life on our planet. In addition to looking back towards these early beginnings, the work explores our immersion in the digital world by reinterpreting natural environments through the screen-based society we inhabit. The study of evolutionary processes is also of great importance as this ultimately evokes a transcendental journey through the past, present and future as well as a fusion of the organic and the technical.
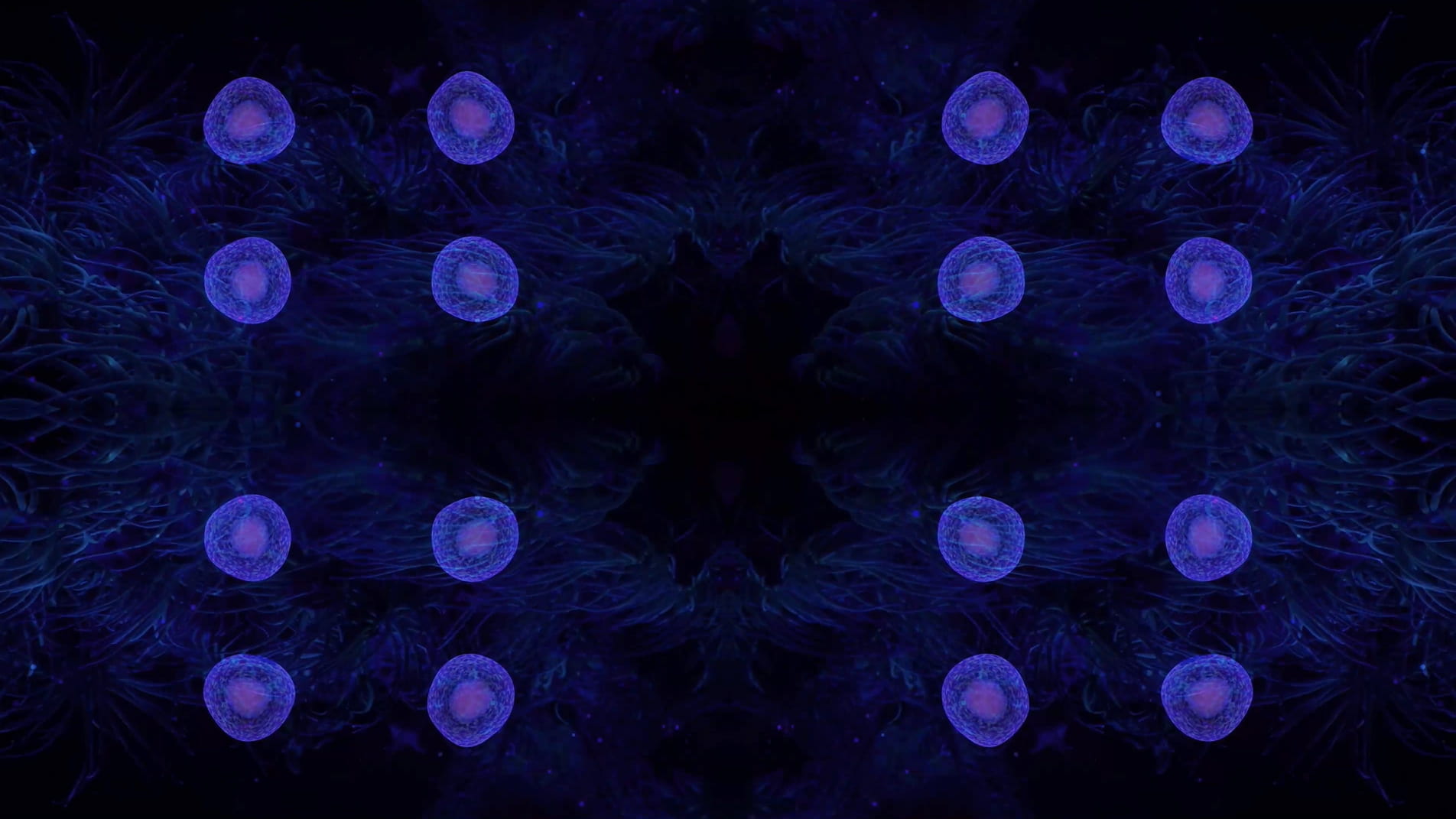

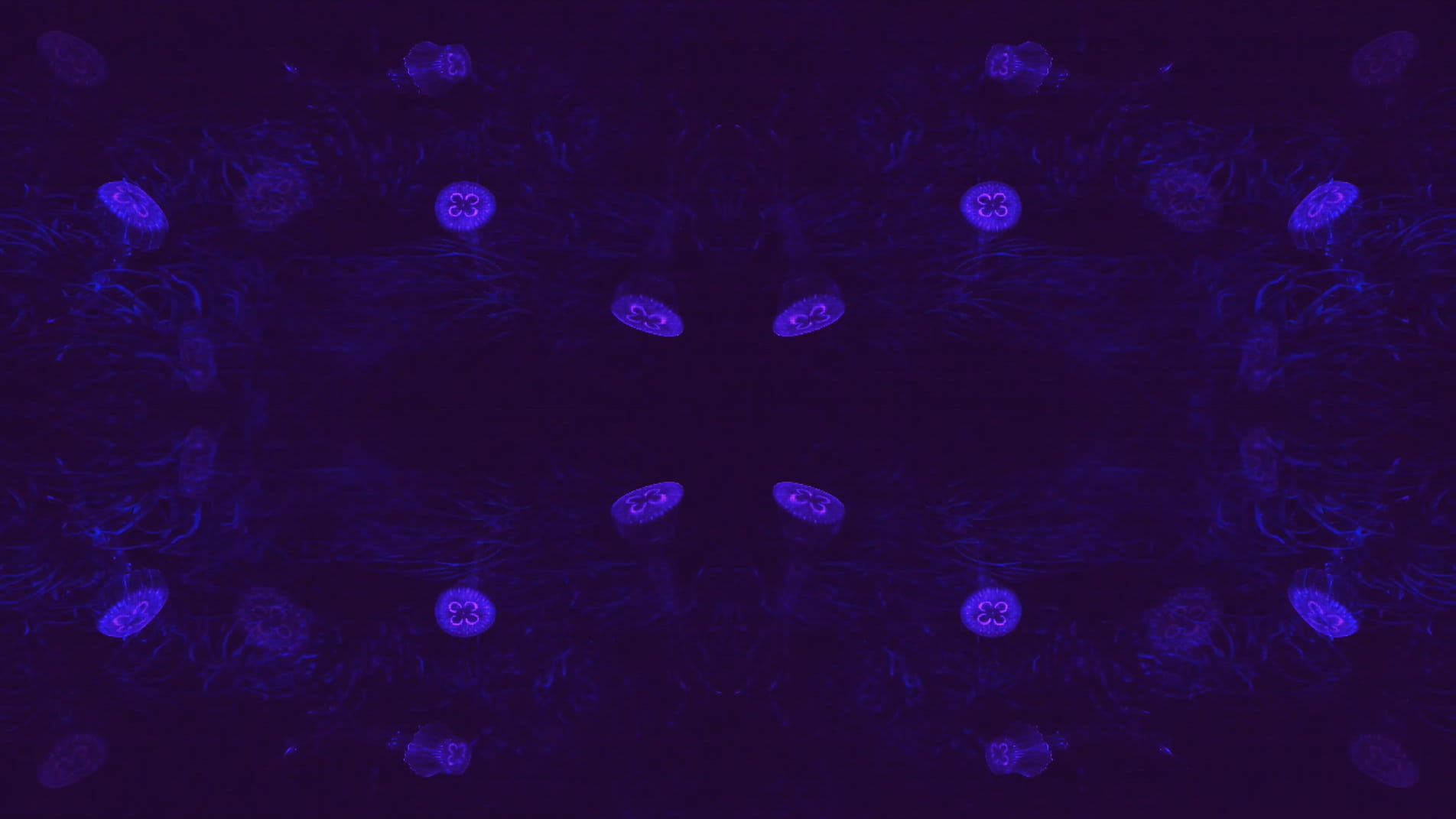
Emphasis is placed upon these themes from the very onset of the piece which opens with an animation of cells dividing, a sequence that delineates a point of origin and the genesis of new life. The cells then fade out of view to be replaced by jellyfish that float across the scene, gelatinous in form with iridescent hues of purple and blue. Although included due to their their correspondence with the cells, the jellyfish are notable in presence since they are one of the oldest species to exist on our planet, residing in our oceans for more than 500 million years. This remarkable timescale predates the dinosaurs and is fascinating in light of my ideas surrounding primal states.

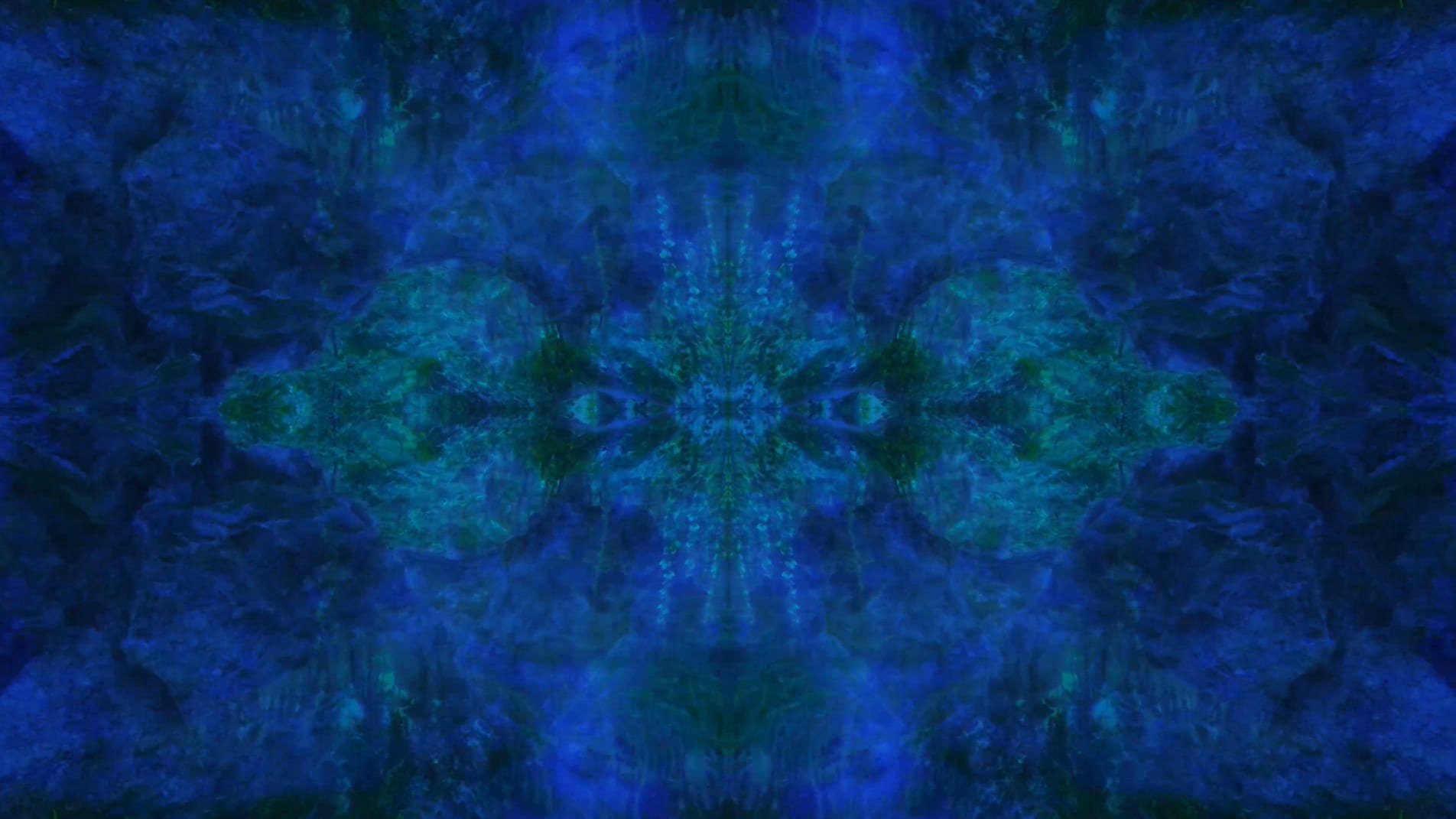
Following this, the video transitions into a haze of violet light which dissipates to reveal the shapes and structures of tree branches, rocks and mountains as scenes of a digital jungle emerge. Moving deeper into the landscape and through the undergrowth, circular patterns begin to appear with organic matter converging into the centre point where the panels of the video meet, creating a hypnotic effect that is reminiscent of a kaleidoscope.

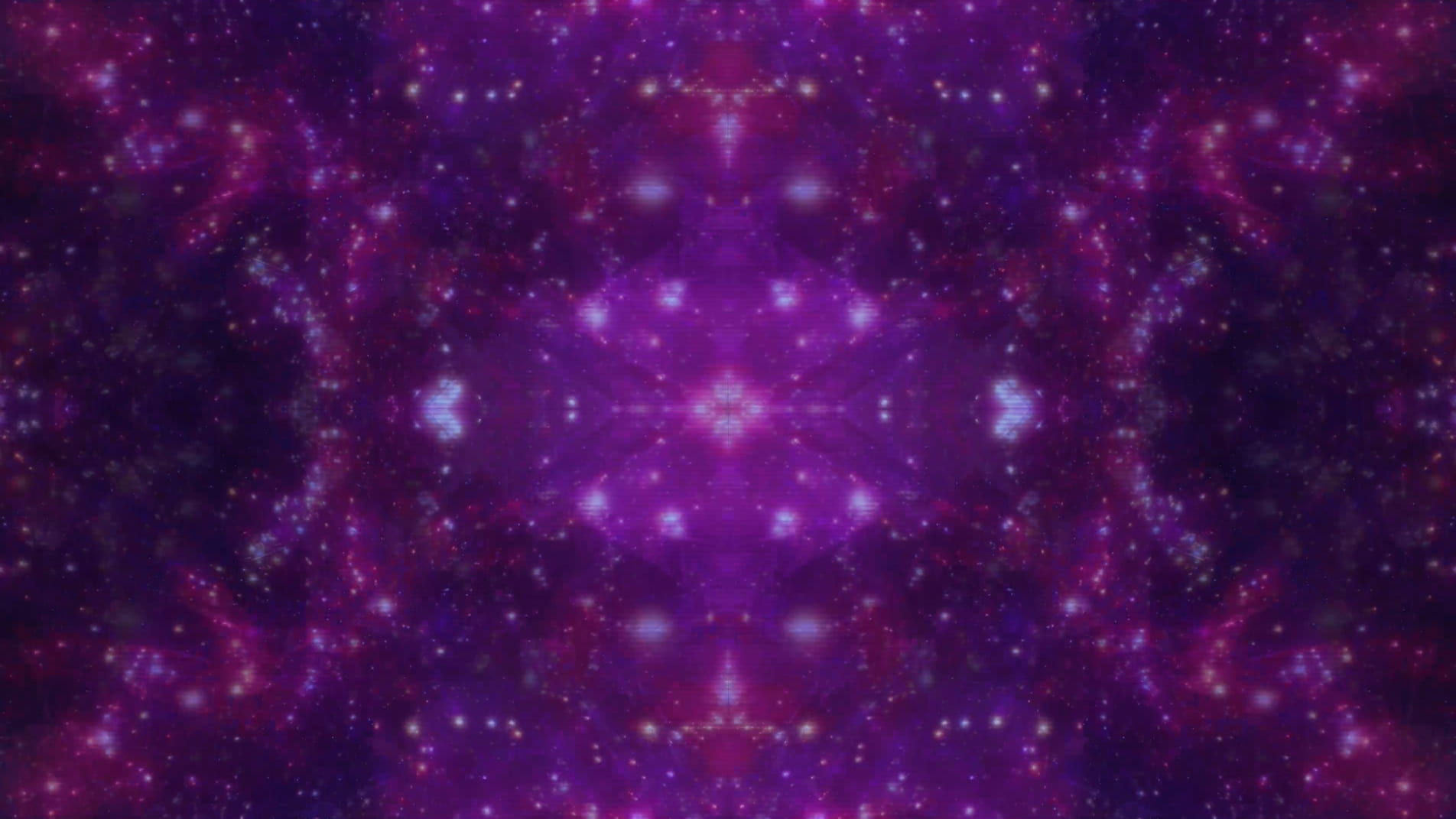
BtL: Do you think your process of digitally constructing the work is important as a way of situating these primitive visual landscapes within the conditions of the 21st Century?
SW: Absolutely. The digital process allows nature to exist in a computational form and suggests that it is not estranged from technology in the way that we might initially imagine. In the text Novacene – The Coming Age of Hyperintelligence, (2019) the scientist James Lovelock reiterates this view. He proposes that ‘computers work purely in zeros and ones; from that they can construct entire worlds … information may indeed be the basis of the cosmos’ (2019: 88). It is this description of the cosmos being made up of information, that is referenced in a literal sense within my work.

This environment visually resembles many of teamLab’s installations such as The Infinite Crystal Universe. Presented as immersive experiences, teamLab encourages us to reach infinity and oneness by seeking to ‘transcend boundaries in the relationship between the self and the world, and of the continuity of time’ (Pace Gallery 2014). Computer programmes and algorithms are widely used in the creation of these works, engendering the belief in a computational universe in the same way that my work intends to.
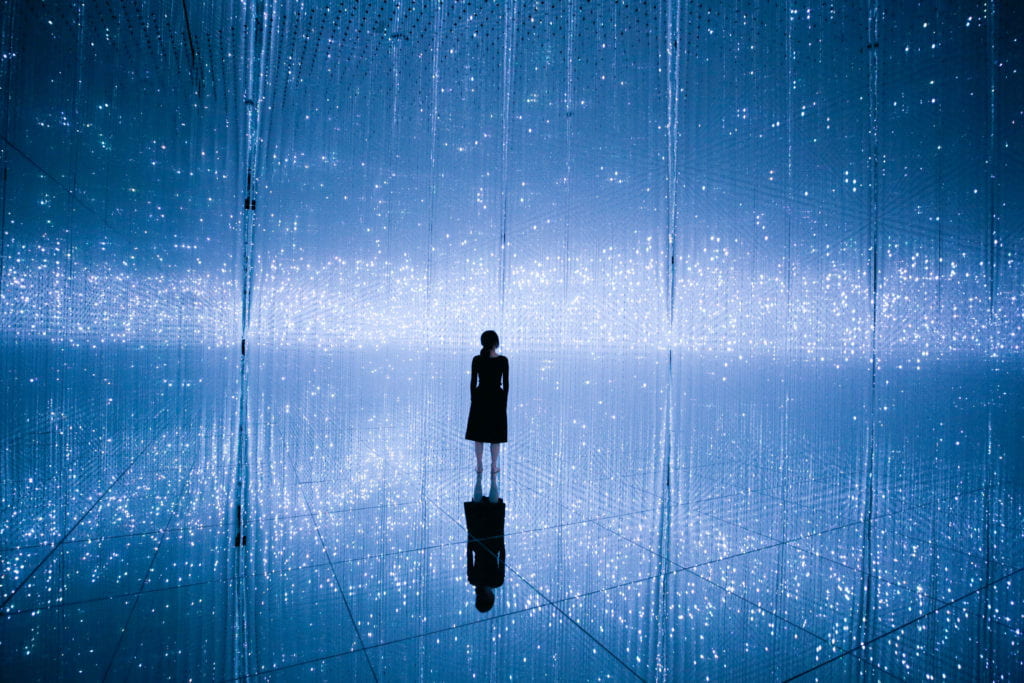

BtL: You seems to situate your visual practice across a variety of thresholds. Can you give us a few examples?
SW: Further influential research includes the concept of the technological singularity, a term first popularised in 1993 with Vernor Vinge’s essay The Coming Technological Singularity. In physics, a singularity is defined as a point of infinity, such as the centre of a black hole, where matter becomes endlessly dense and physical laws break down, resulting in the merging of space and time. In relation to this scientific definition, the theory of the technological singularity hypothesises that we will soon cross a threshold where machine intelligence will surpass biological intelligence, an advancement that will lead to irreversible changes to civilisation.
Ray Kurzweil, futurist and author of The Singularity is Near: When Humans Transcend Biology, suggests that ‘machine intelligence could become indistinguishable from that of its human progenitors within the first half of the twenty-first century’ (2005: 3). What this will look like for humanity is unclear as both a dystopian and utopian scenario would be possible. Either way, it is the notion of transcending current limitations that is most intriguing. It is also speculated that the universe began by such an event, meaning that there was a singularity in our past as well as one potentially in our future, demonstrating the way history repeats itself in a loop.
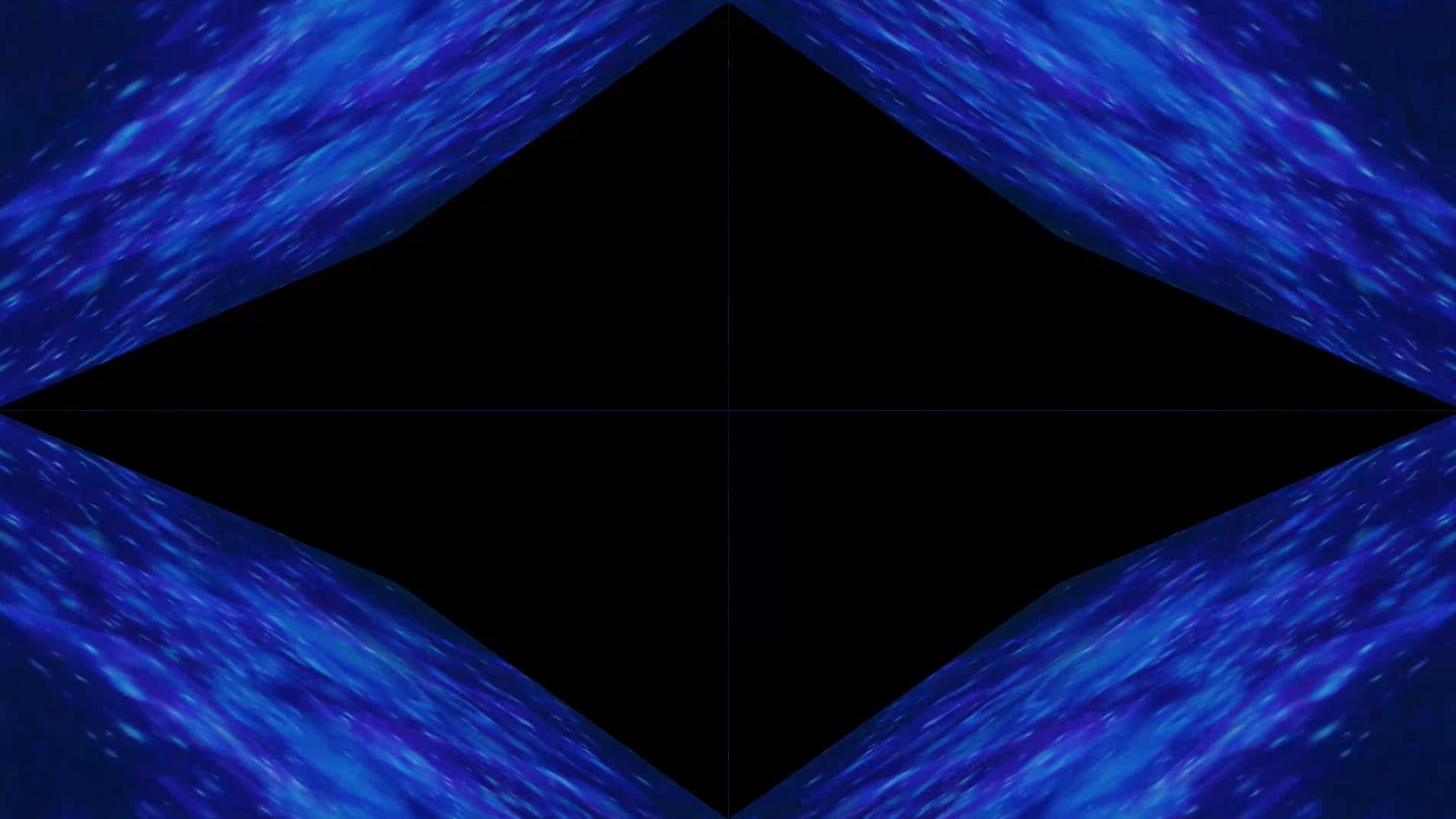
This notion of the singularity manifests in Primordial Loop when the screen becomes increasingly pixelated and the motion accelerates, referencing the exponential rate that we are approaching what is often referred to as the ‘event horizon’ (Kurzweil 2005: 7). Once this is reached, the centre of the screen unfolds to reveal a passage into a new space-time dimension.
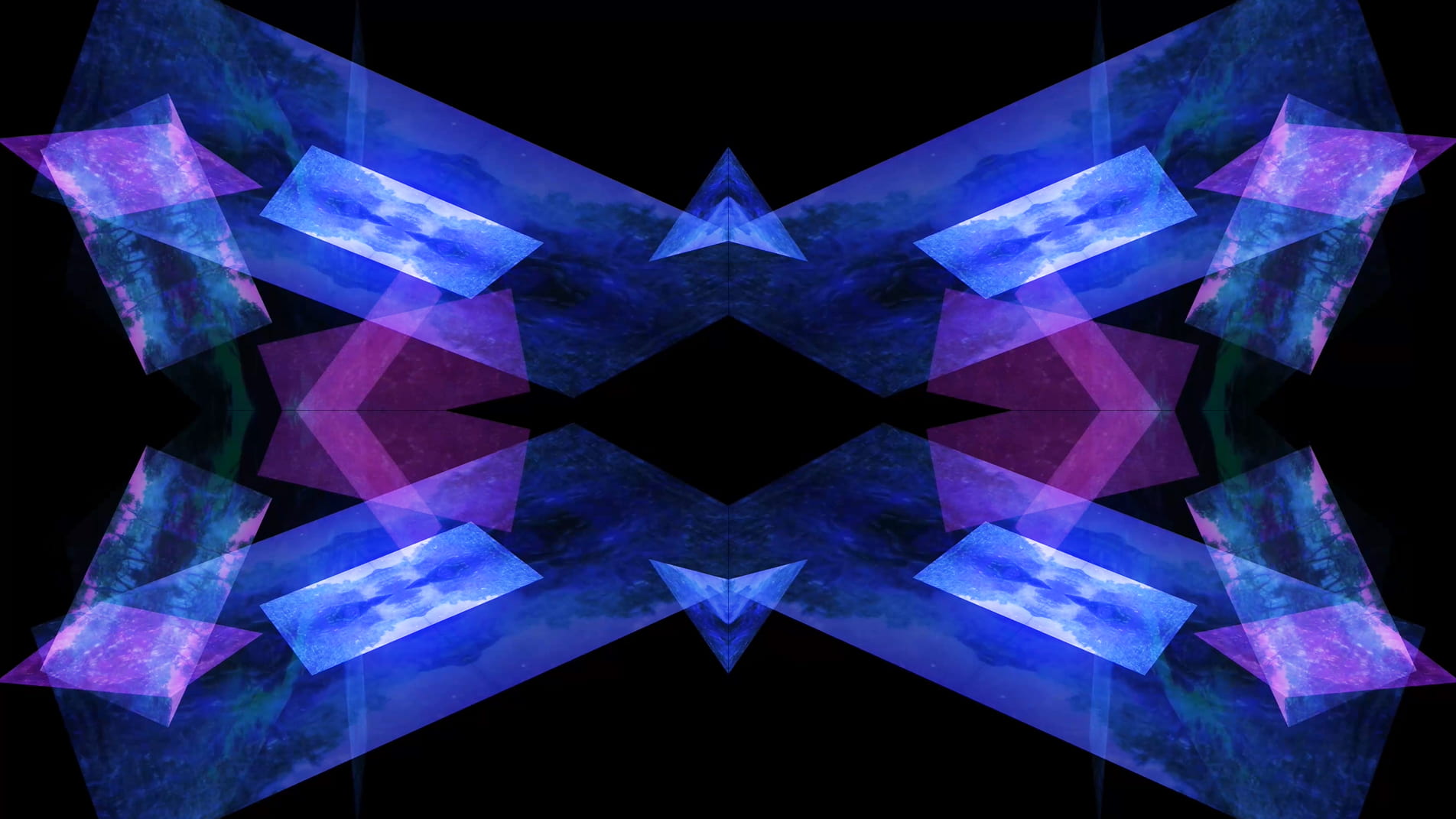

The final scene reveals the culmination of this journey into a post-singularity state. The video fragments, breaking apart from its original structure and transforming into multiple screens floating within a dark void. The plurality of the work opens up new ways for it to exist, with the panels constantly moving across the X, Y and Z axes. The music also shifts from its electronic sound to something choral and celestial. At this point in the video, space is perceived in a more fluid way, it bends and stretches, becoming something that we develop a heightened awareness of.
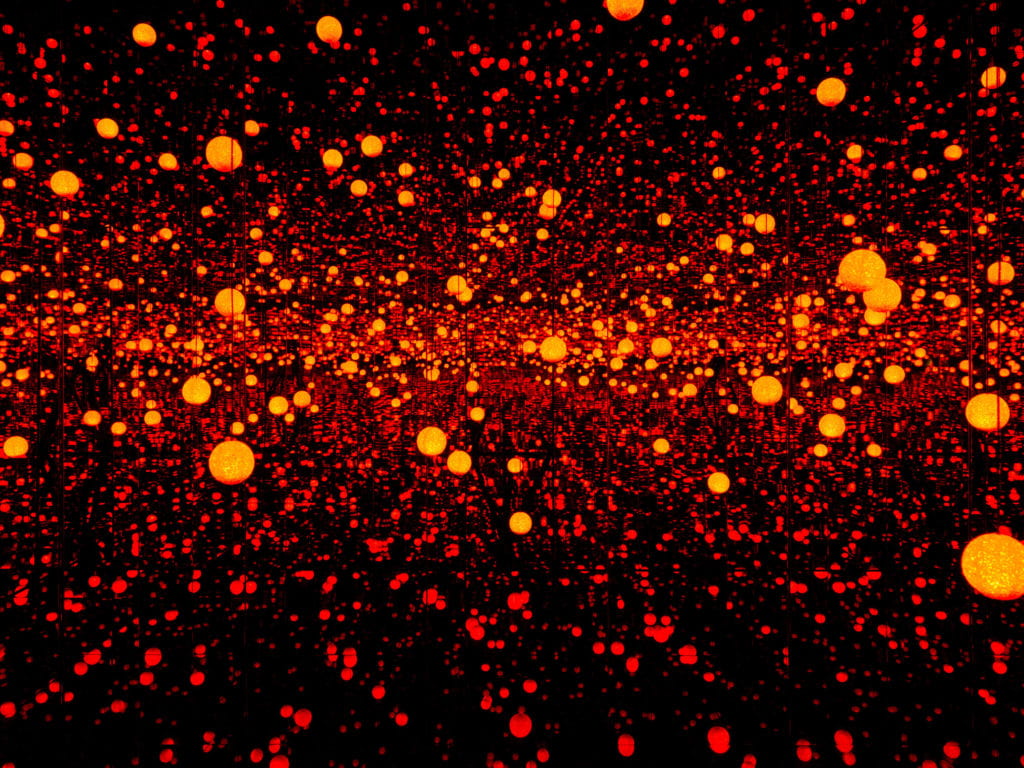
This exploration of a boundless existence relates strongly to Yayoi Kusama’s Infinity Rooms, another key inspiration for my practice. The installation, Dancing Lights that Flew Up to the Universe, is described as a perceptual experience that functions as ‘a harmonious and quiet place for visitors to contemplate their existence, reflect on the passage of time, and think about their relationship to the outer world’ (Hirshhorn 2017). The title of Kusama’s piece acts as an expression of hope and resonates with my own feelings of reverence for the infinite. A sense of spirituality is embodied within the ending of my work, suggesting that it has indeed transcended in the same way that it is predicted that we, as humans, will one day transcend our own experience of reality.
BtL: The photographic strand of your practice, titled Merge/Melt, seems to explore similar notions to Primordial Loop through amalgamating technological and natural elements to create something that exists in a transformed state.
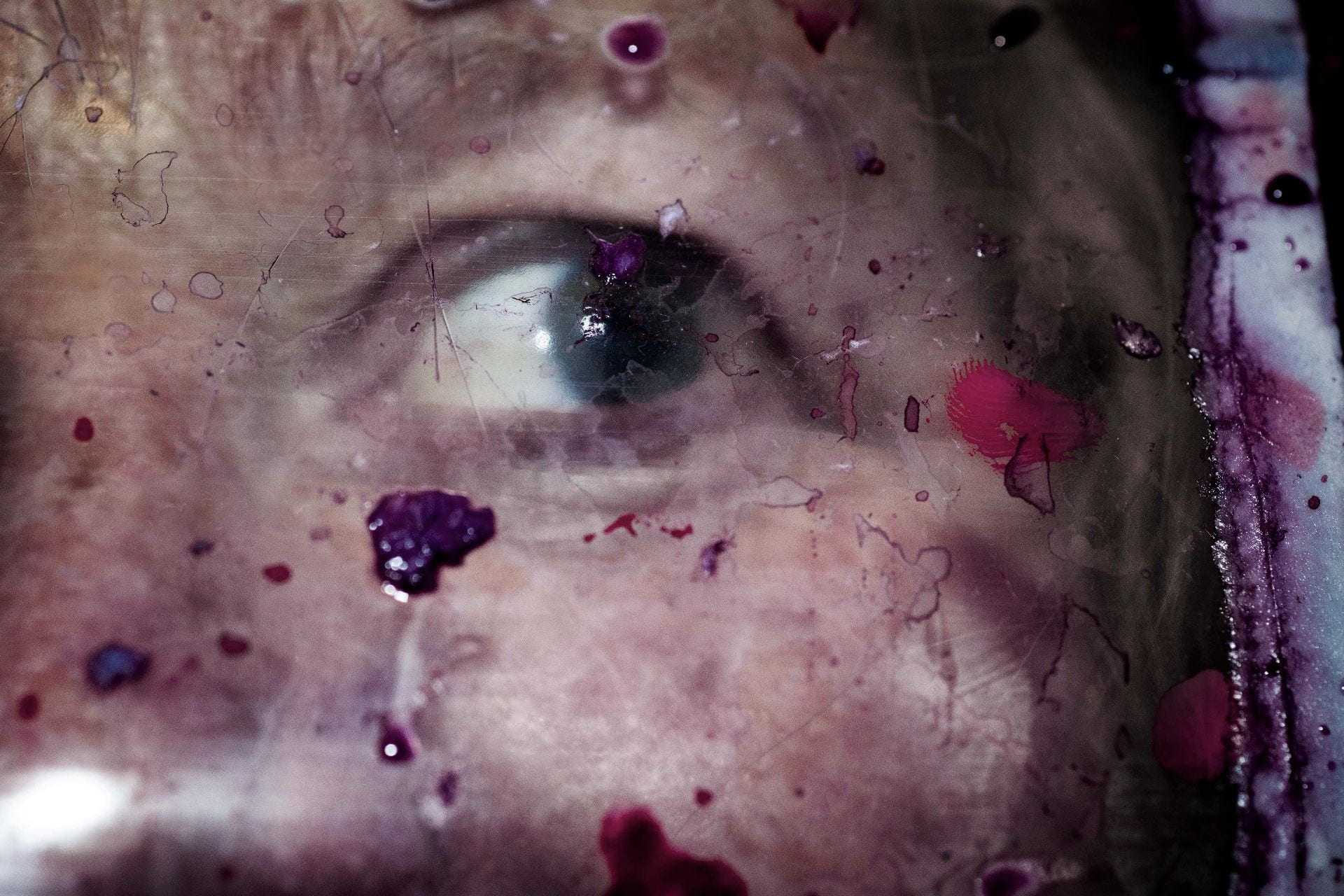
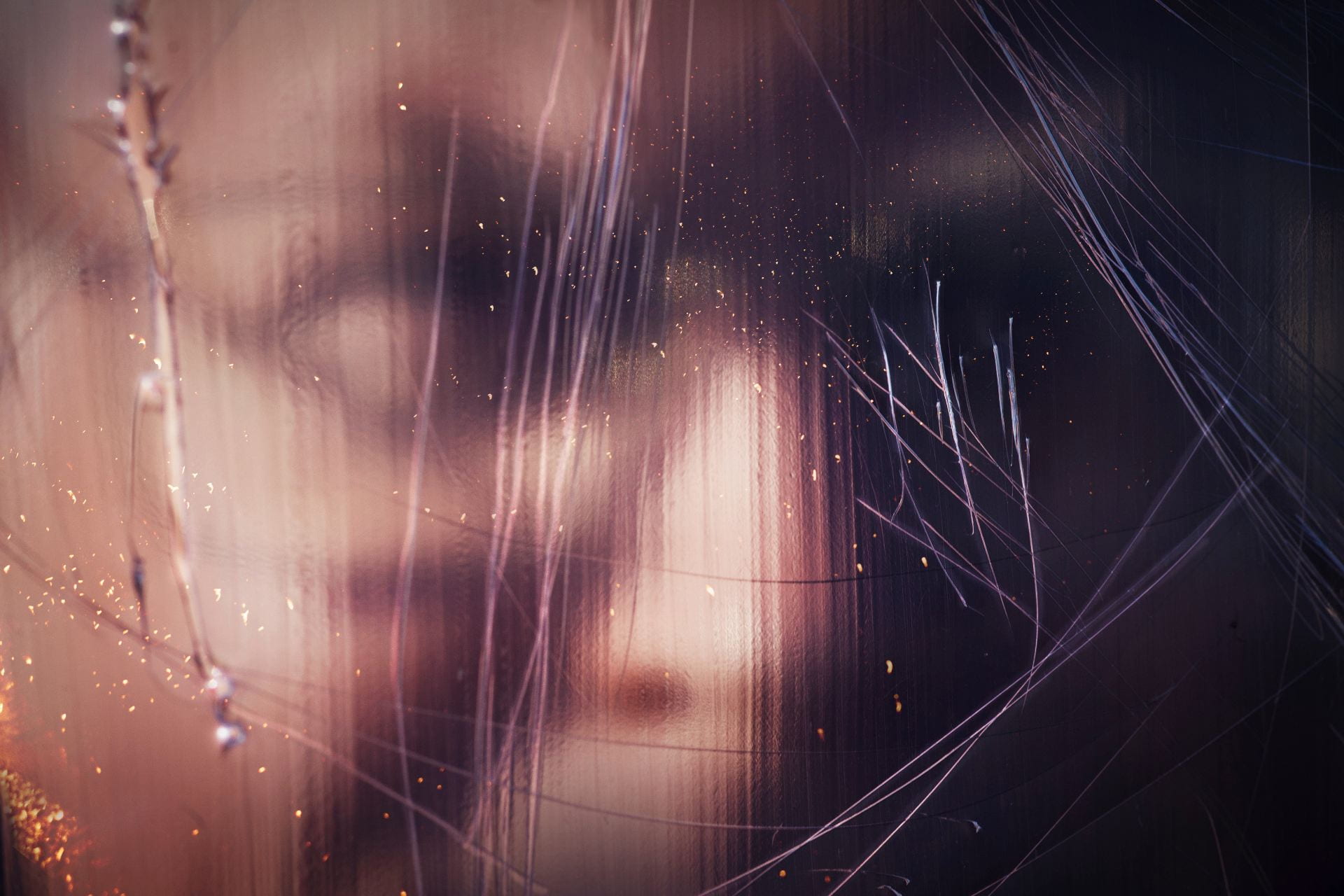
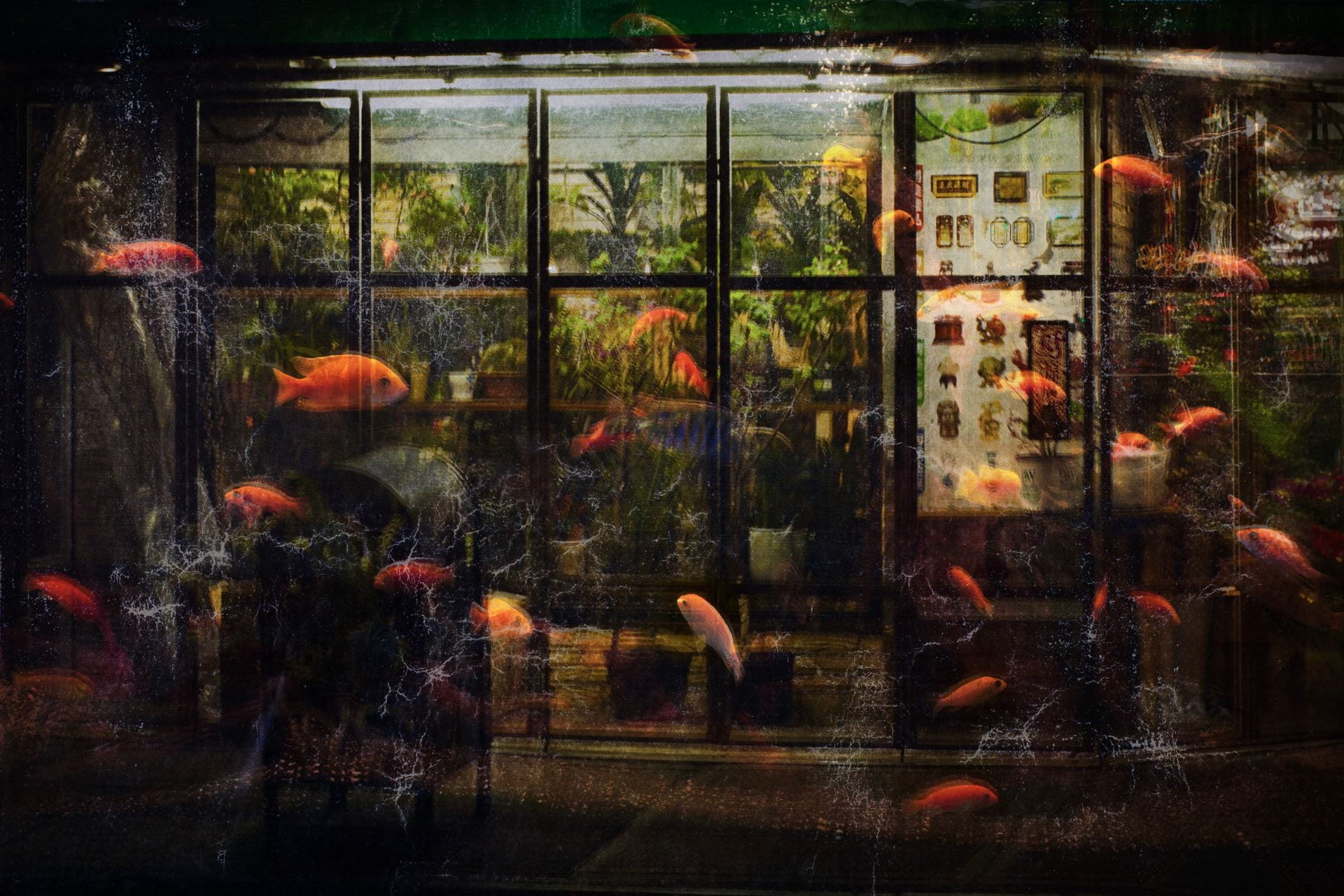
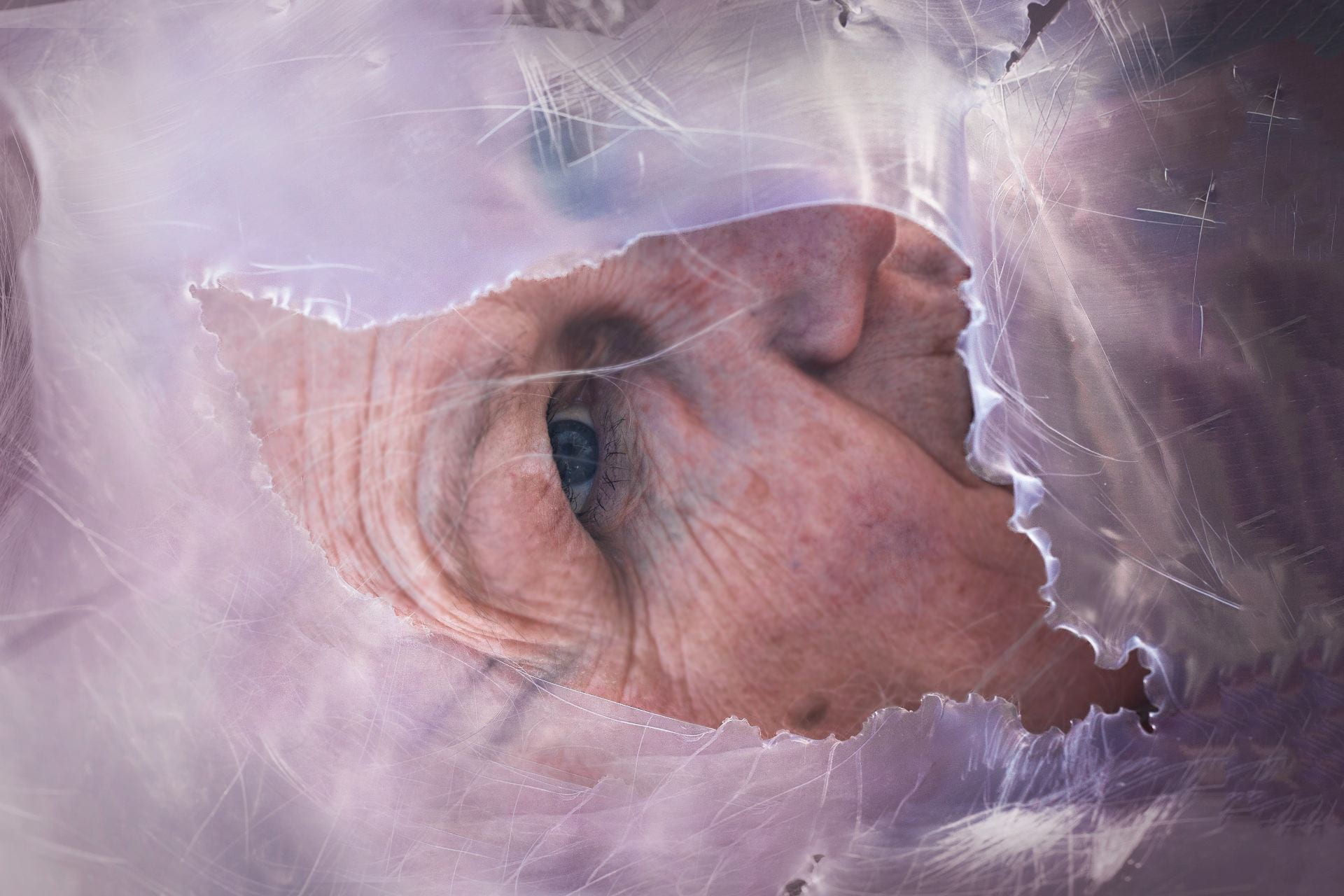
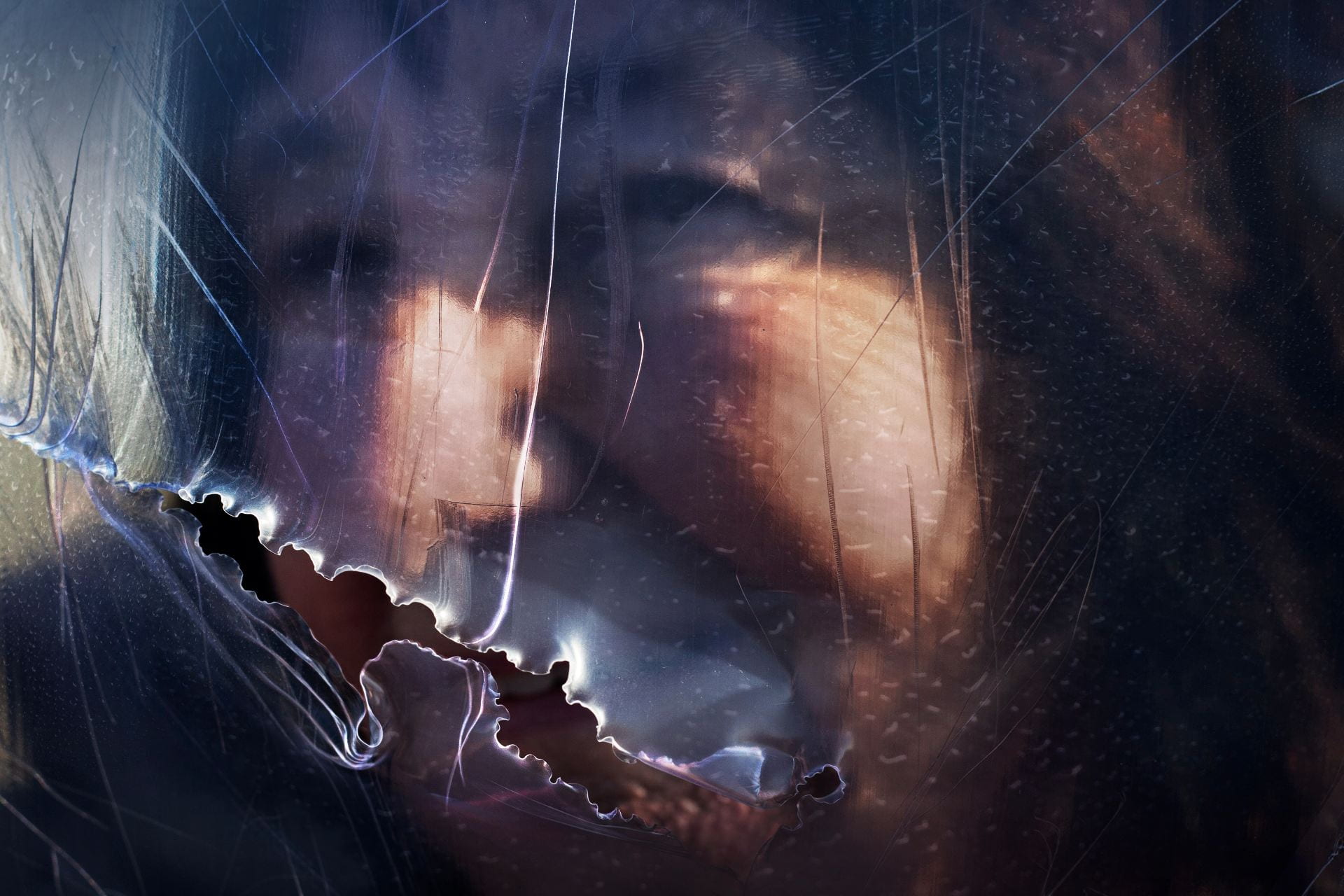
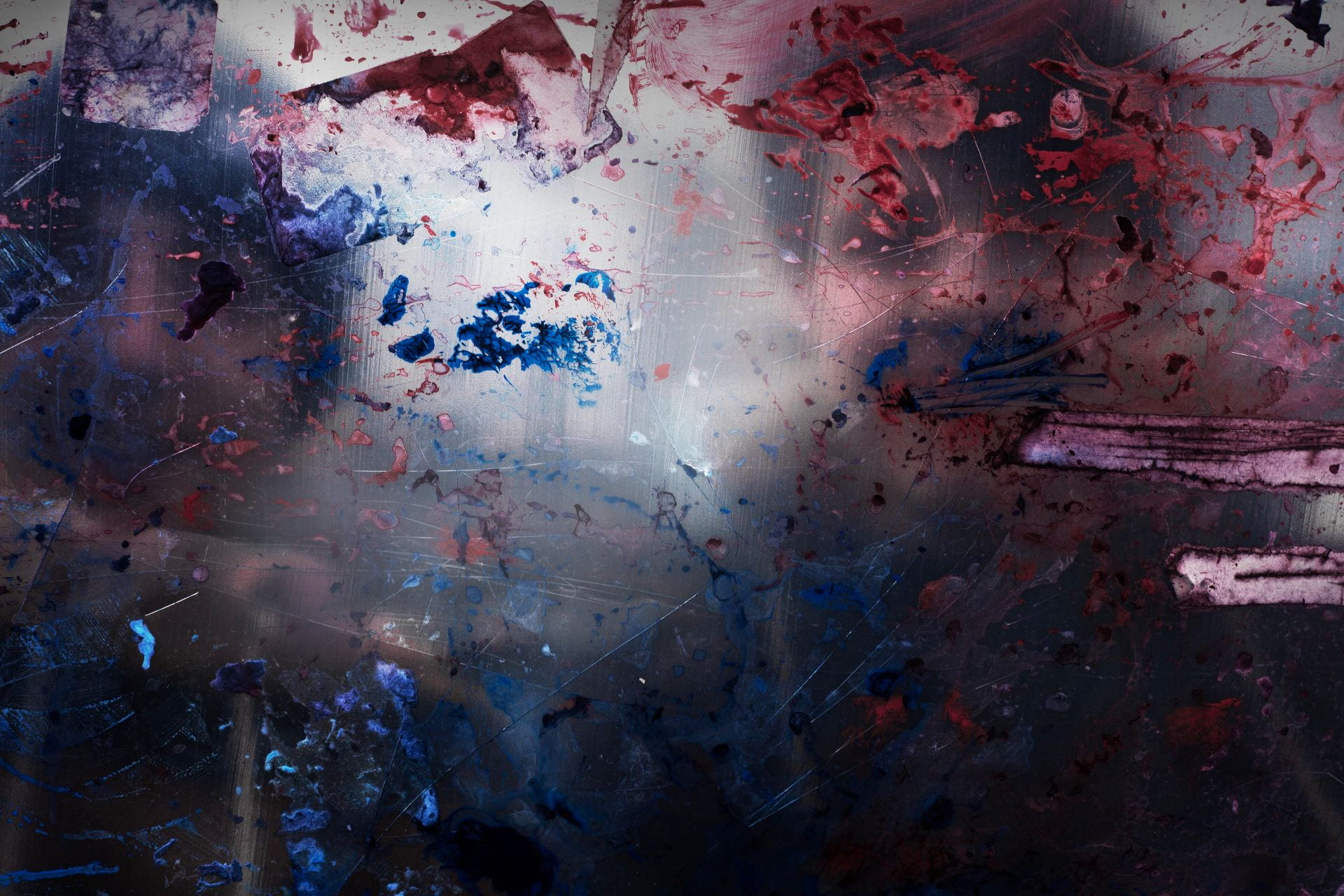
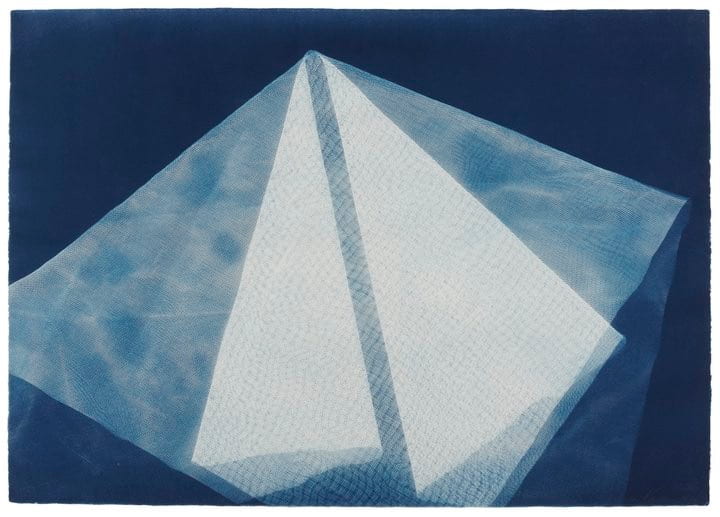
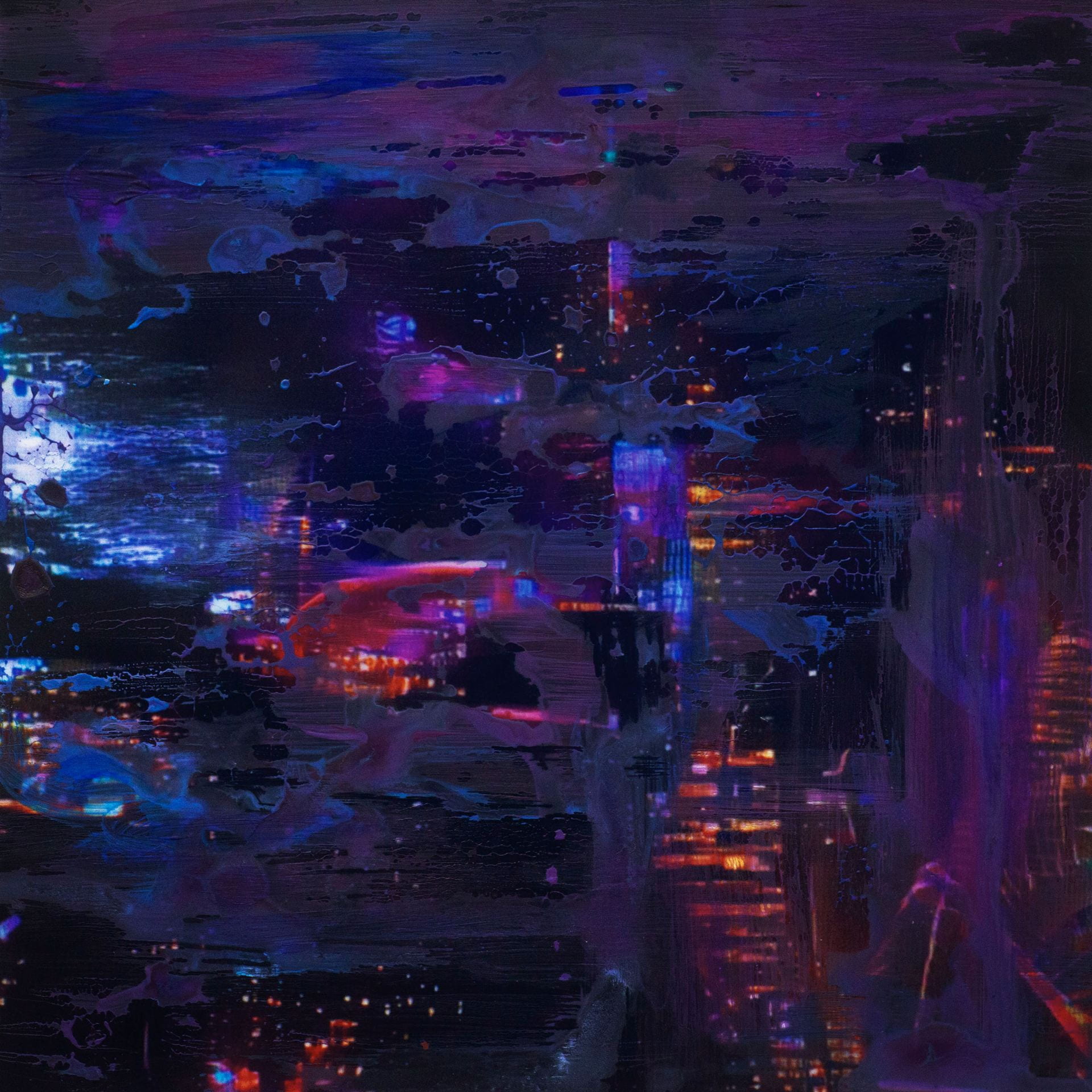
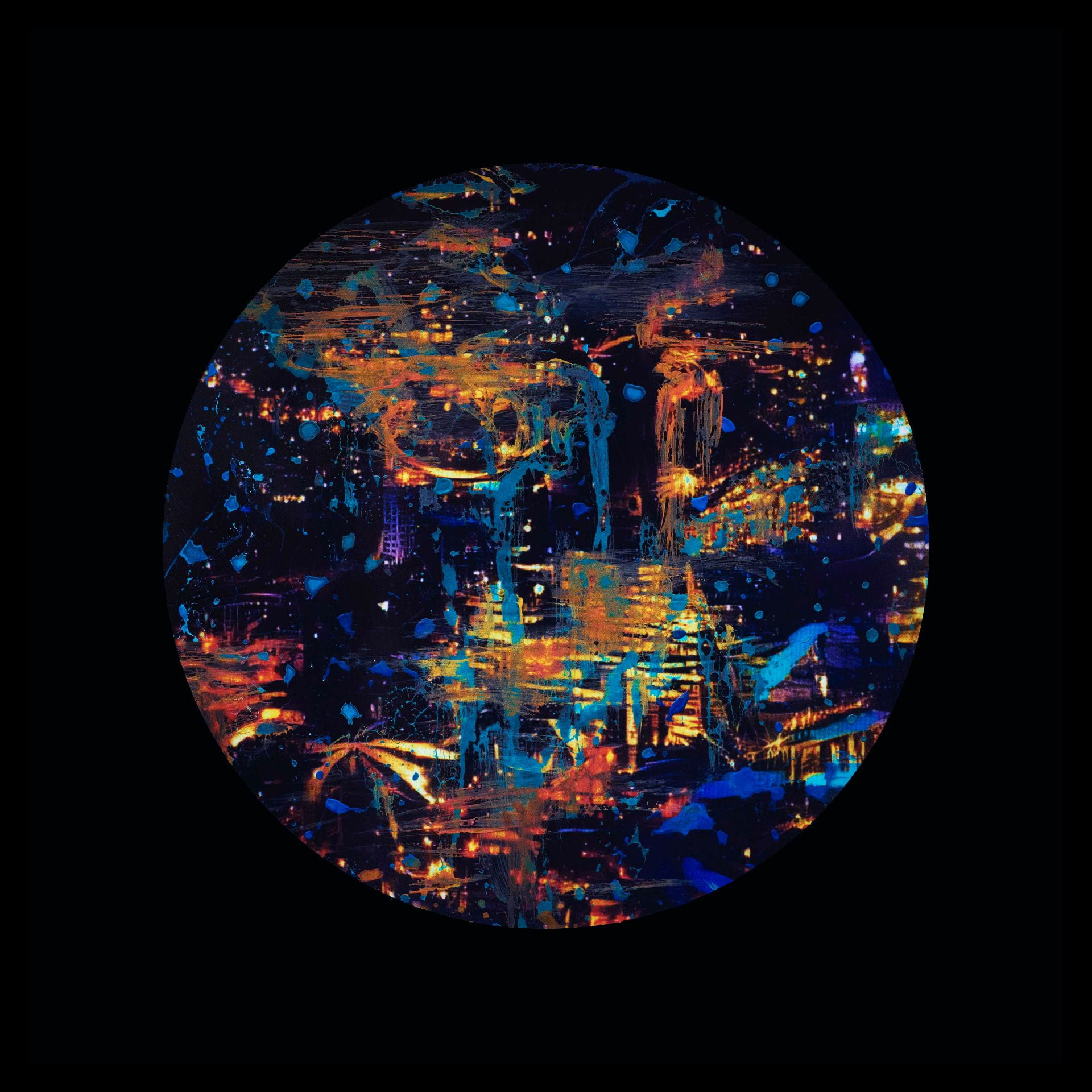
SW: Merge/Melt experiments with the use of digital tools to build new forms and structures, revealing warped patterns and textures that suggest the physical world is melting into an electronic one. During the production of the series, photographs of jungles and cityscapes were fed into an algorithm and then merged together to generate new entities.

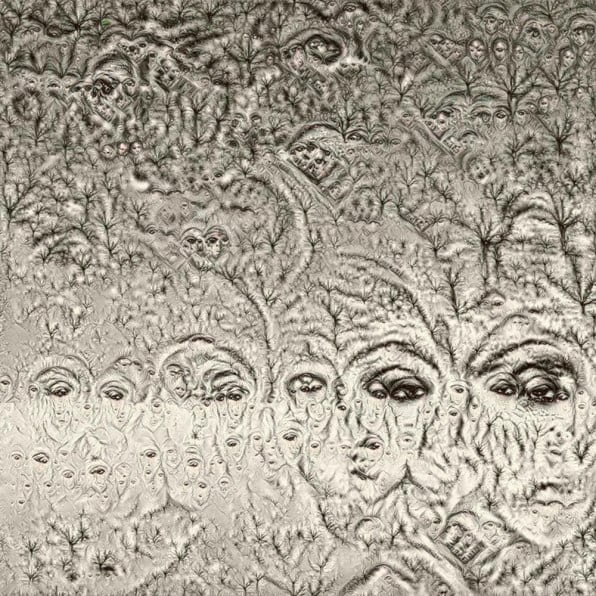
The Deep Dream algorithm was used specifically for this purpose as it was able to draw out interesting shapes within the depths of the images. Deep Dream is described as a convolutional neural network and was originally developed in 2015 as a means of providing AI researchers with an insight into what an algorithm sees when it analyses an image. Since its inception, however, it has primarily been used as an artistic tool with results that are psychedelic in appearance. The artist Mario Klingemann is one of the pioneers of working with neural networks in this way. The works Archimedes Principle and Parting From You Now, draw attention to the pareidolic details that can emerge from an image, in the same way that humans are able to observe random shapes in passing clouds. The ability of Deep Dream to provide an algorithmic vision of our environments relates to the computational form of nature seen in Primordial Loop, epitomising the suggestion that ‘computation is existence’ (Lloyd and Ng cited in Kurzweil 2005: 342).


BtL: There is appears both a visual and conceptual fluidity to your practice, yet also a sense of chaos and the unexpected.
Artist and theorist Joanna Zylinska’s text AI Art: Machine Visions and Warped Dreams also feels especially relevant. Zylinska refers to algorithmic art as ‘an ouroboros-like circle of random variations’ (2020: 72), a description that encapsulates the chaotic nature of my work but equally observes the connectivity that is so integral to its construction. The effect of this merging process is the predominant feature.
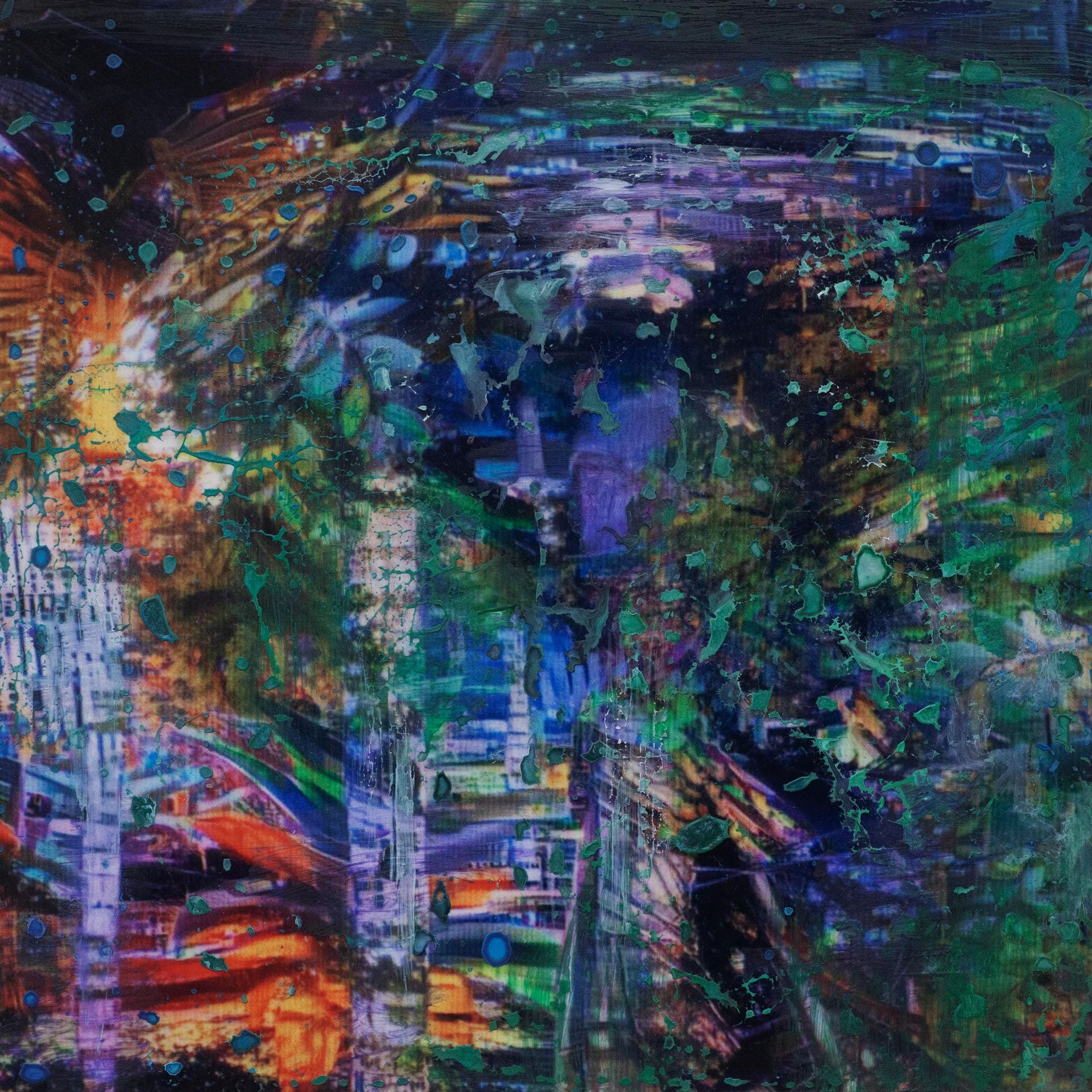
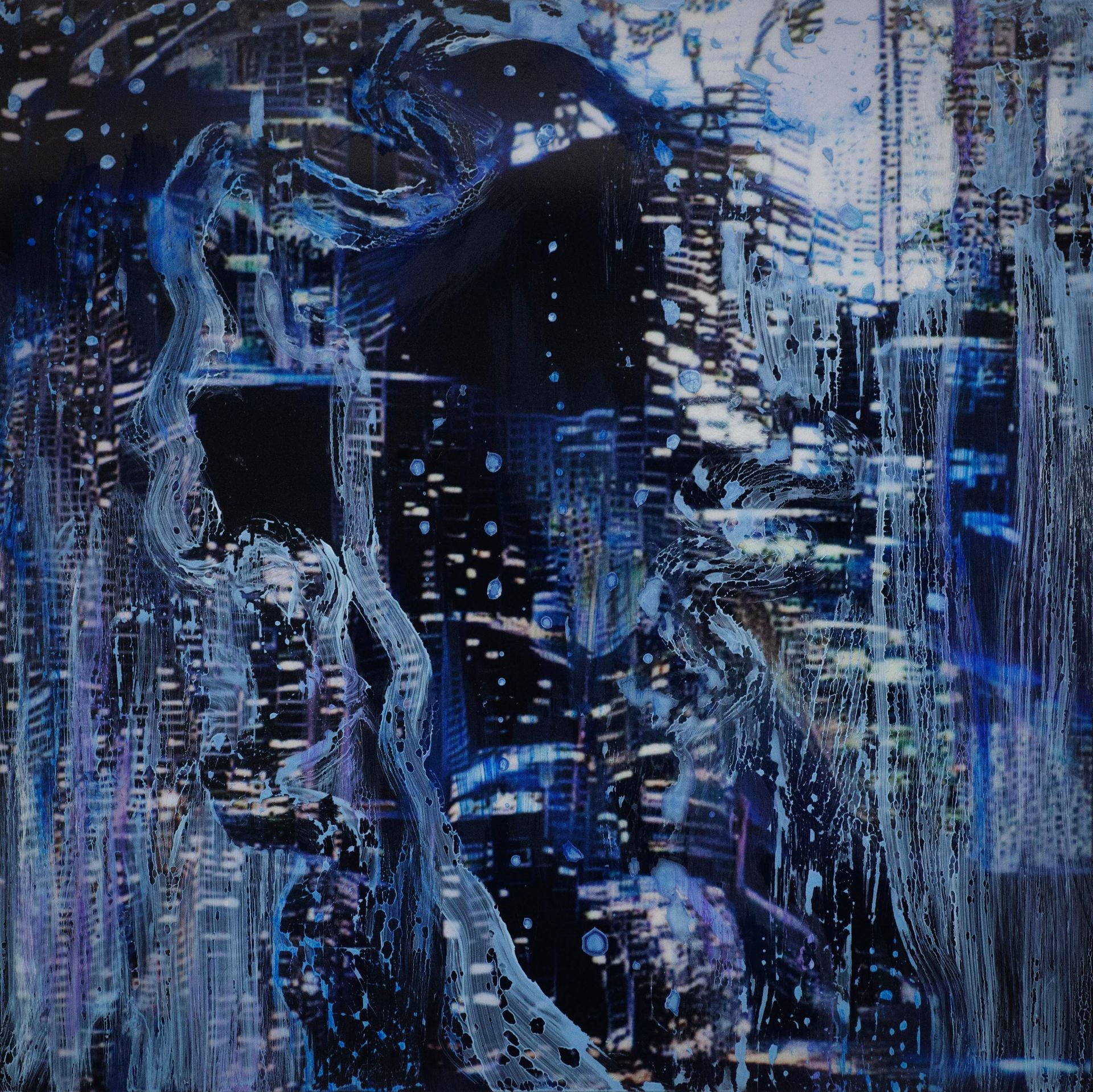


In some images, it becomes difficult to distinguish city lights from stars as the sky dissolves into the architecture and structures blend together like coloured inks, a liquid yet luminous appearance that could almost be the result of street lights reflected in a pool of water. Due to the alteration and enhancement of certain hues, some of the images look more industrial and synthetic whilst others, with jewel bright shades of green and blue, are more jungle-like, allowing each composition to exist on a continuum between metropolis and nature. It is this fluctuation that I find most inspiring as it underscores my interest in the creation of multiplicities.
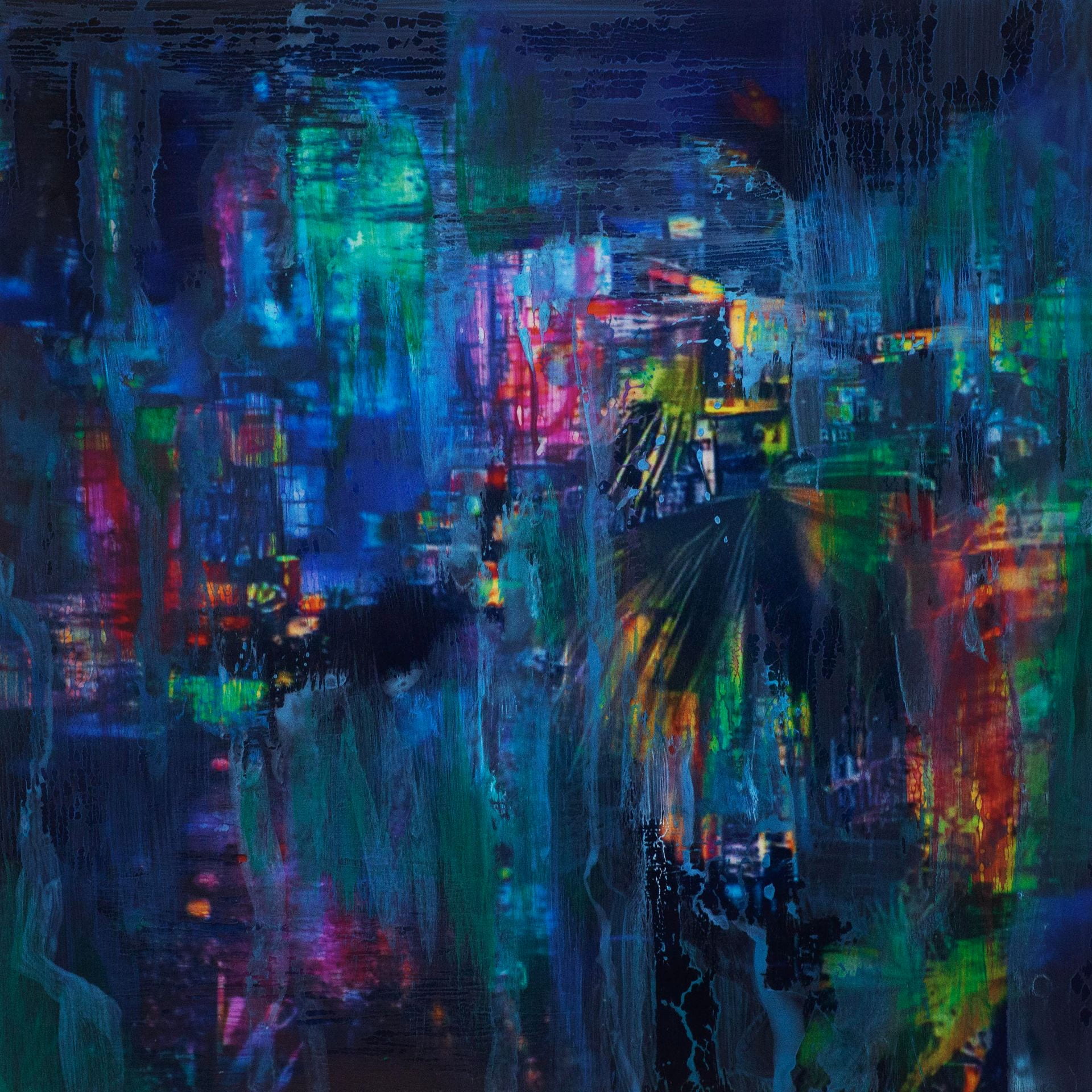

To clearly communicate a sense of things evolving, I present my images as animated video sequences on screens and opted for a circular format in order to create a stronger comparison to the concepts explored in Primordial Loop. These circular shaped pieces embody a more pronounced mutability and link back to Zylinska’s reference to the loop of the ‘ouroboros’, reflecting wholeness and infinity. They additionally have the look of portals, perhaps acting in a similar way to black holes. This creates a further parallel with my video piece which also leads us through into a new dimension.

BtL: You are a graduate of the BA Photography course at Falmouth University. Any tips or advice for current / prospective students?
SW: My advice would be to view university as a time to experiment with photography, to try out new ways of working and push the boundaries of the medium. Over the course of my three years at Falmouth, I feel fortunate to have been able to expand my practical image making skills, both with analogue and digital processes. Although it can be strange to do something unfamiliar, I would completely recommend it as it will enable you to develop new areas of interest and gain a broader experience of the arts. And, it goes without saying, to make the most of the university facilities and technical workshops in addition to opportunities for collaborative working whilst you are a student as this provides invaluable support.
BtL: What can we expect from you next?
SW: I am planning to develop more work that expands upon the themes seen Sensorium and incorporates a variety of techniques, I will be continuing to practice in other visual disciplines alongside my photography. In addition to lens-based media, i will be continuing to branch out into other areas such as painting, sculpture and installation – and continuing to experiment. Who knows?