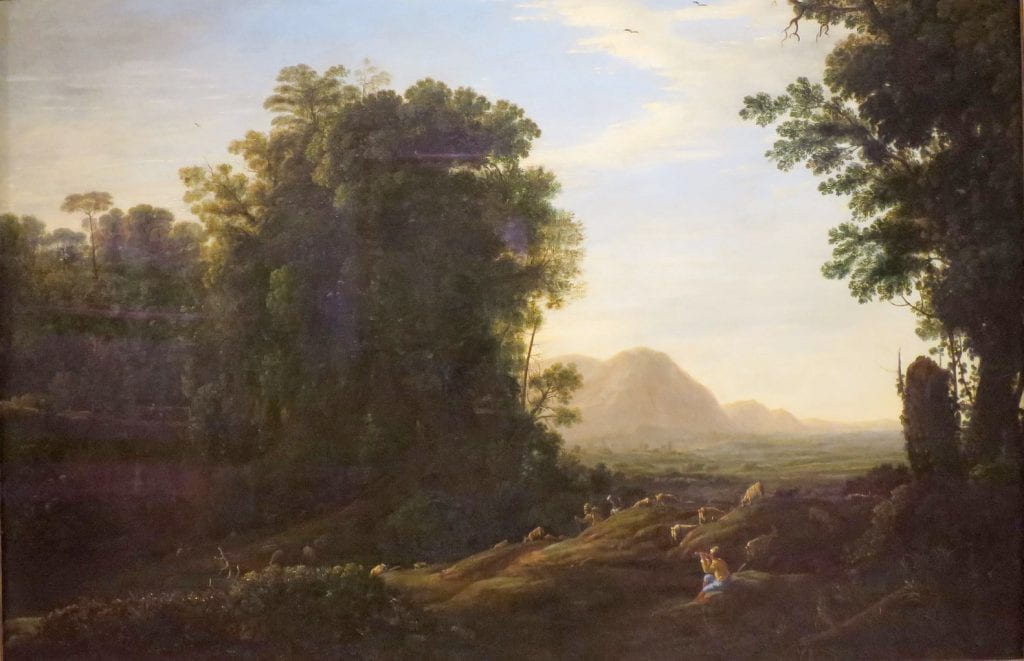
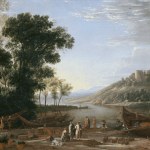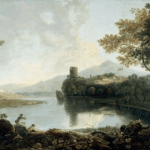a MYTHOlogical Arcadia (or not?)
‘Does landscape photography remain encoded within the language of academic painting and the traditions of landscape art which developed during the 18th and 19th Centuries’? (Clarke, 1997, p.55)

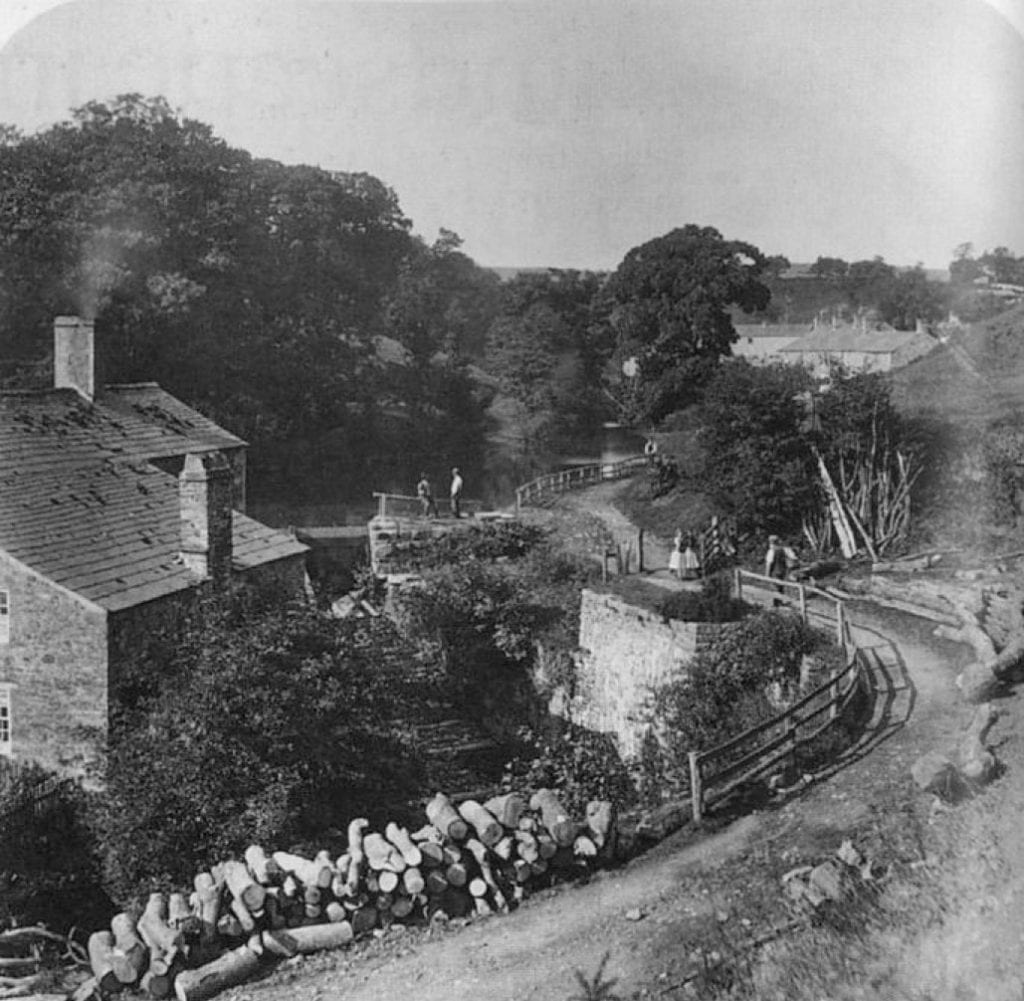
In this session, participants are encouraged to consider a historical relationship between painting and photography in the context of thier own landscape environment. They will consider ideas of the Picturesque and considerations are made as to how such visual mofifs may be culturally / visually reproduced to create a myth of the constructed land as a rural arcadia – as it is transformed into a land-scape.
Participants are encouraged to independently research the Pictorialist movement in photography and the work of Peter Henry Emerson
‘A ‘landscape’, whether cultivated or wild, is already artifice before it becomes the subject of a work of art. Even when we simply look, we are already shaping and interpreting…Landscape pictures will breed landscape pictures.’ (Andrews, 1999, p.1)

This Session could be run in conjunction with:
- Places with a Past
- Tell Me a Story (Again)
- Postcards from Home
- A Sublime Sight – post to come
‘Whether noble, picturesque, sublime or mundane, the landscape image bears the imprint of its cultural pedigree. It is a selected and constructed text’ (Bright, 1985)

Aims & Outcomes:
- To consider vernacular / stereotypical representations of the local environment / landscape
- To investigate the relationship between painting and photography as it applies to representations of the land
- To understand the nature of the picturesque as it applies to photographs of the land / a ‘tamed’ land
- Participant Outcome: 1 10×8 digital print

‘The picturesque is enlisted in the definition of what the country means: it becomes a patriotic term, a touchstone of national characteristics’ (Taylor, 1994, p.25)
You will need:
- Digital cameras for all participants (and appropriate memory cards) *This session can also be run using Camera phones or Lumix cameras
- Card readers
- Access to computers (or laptops)
- Tripods
- Flashguns if you plan to practice lighting techniques
- An Introductory Brief & Presentation (below) for participants to outline the ideas and provide examples
- A booked room to critique participants work (either via a projector or via print)
- Blue tack to pin the work
- Costings and Risk Assessments

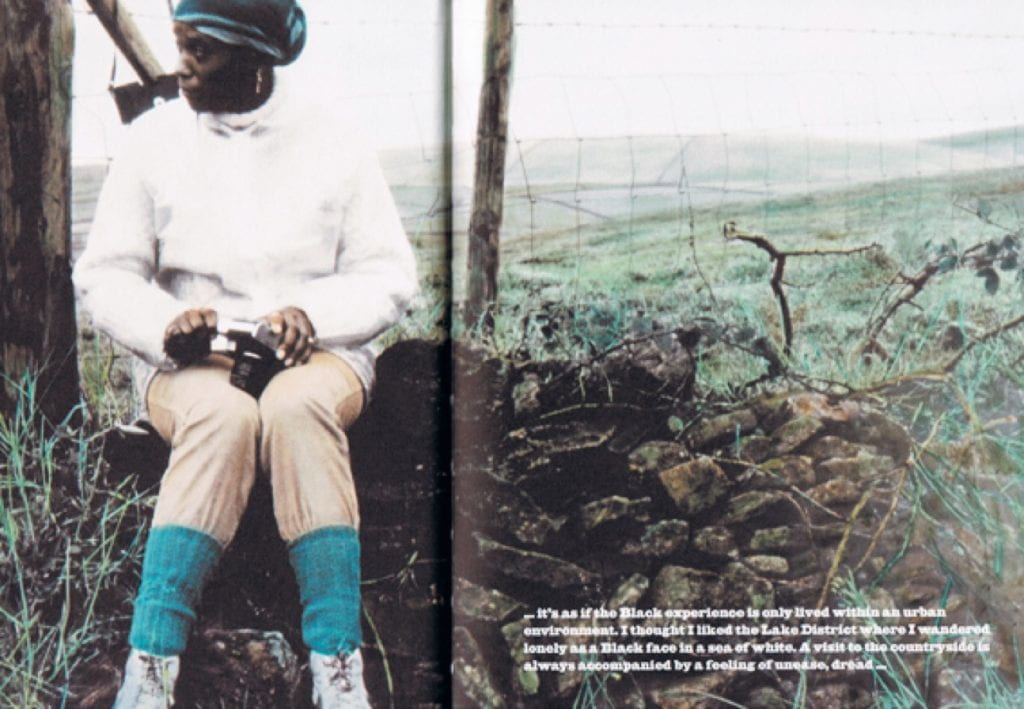
‘The act of naming is an act of taming. From its inception photography has been involved in investigating and detailing environments, helping culture to appropriate nature’ (Wells, 2011, p.3)
Research: Pictorialism & work of Peter Henry Emerson
Preparation Work:
- Ask participants to read Fergus Heron (2018) ‘Built Worlds: Photography, Landscape &. Different Natures’ from Photography & Landscape / The Photographers Gallery available here
- Ask participants to watch Jem Southam in Conversation (2014) from the onLandscape Conference / Green Room available here
- Ask participants if they have thier own digital cameras and cards
- Make sure you have access to computers / image editing software
- Make sure there are enough team members to support participants (never assume thier prior knowledge)
- Decide whether you will project the work or print it.
- If you are printing it make sure the Photo Lab are aware and be aware of timekeeping so they have space to print the work.
- *If you are running this session off campus, make sure there is access to printers or projectors

‘It is no longer a question of imitation, nor duplication, nor even parody. It is a question of substituting the signs of the real for the real’ (Baudrillard, 1994, p.2)
Presentation Ideas: A mythologicAL Arcadia (or not?)
suggested Session Outline: